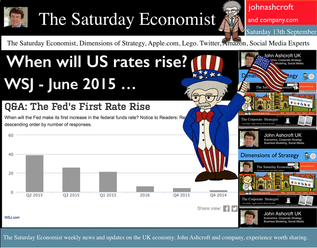
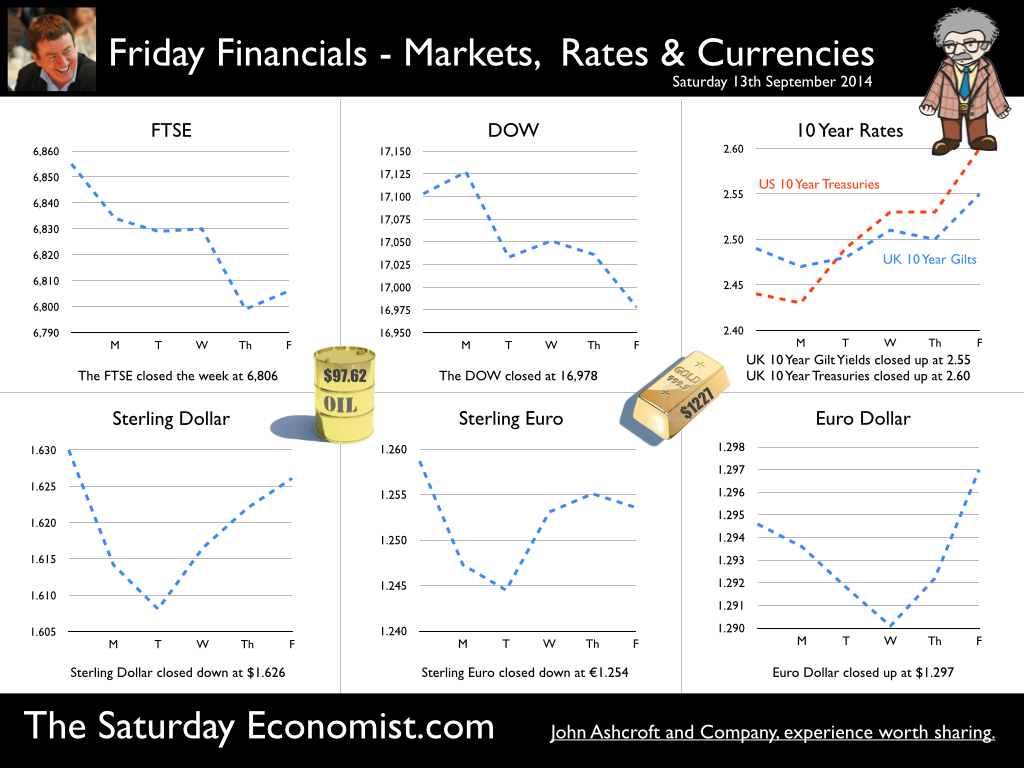
 USA ... When will US rates rise? According to the latest survey in the Wall Street Journal, most economists expect the Fed to raise rates in June next year. 40% expect rates to rise in the second quarter and almost half expect the rise to be delayed until the second half of the year. Positive about the prospects for growth in the US, economists believe concerns about Europe and challenges in the Ukraine suggest the Fed will be anxious to hold the rate rise for as long as possible and well into the year ahead. Mark Carney in Liverpool … The Governor was in Liverpool this week speaking to the TUC Annual Congress. Reassuring union members he and 3,600 staff in the Bank of England were paid a living wage, the governor went on to explain the “judgement about precisely when to raise Bank Rate has become more balanced”. “With no pre set course, the timing would depend on the data.” This week, the data suggests there will be no pressure to increase rates anytime soon and probably not before the end of the year. Oil Price … Fears of inflation abate, as the oil price fell below the $100 dollar mark. Despite turmoil in Iraq and Syria, Oil Price Brent Crude closed at $97.62. The average price in September last year was $112. UK manufacturing prices and headline inflation rates will soften as a result. For the moment, the Saudi swing producers are relaxed. The seasonal low will impact and prices will take the hit. Restoration to the $100 - $110 band will follow in the Autumn, demand and supply will adjust to ensure this is the case. Manufacturing … UK Manufacturing output increased by just 2.2% in July after growth of 3.5% in the first half of the year. Output of capital goods and consumer goods was surprisingly week in the month. We have downgraded our forecasts for the third quarter and the year as a whole (3.4%) as a result. Construction output ... UK Construction output growth slowed to 2.6% in July after growth of 6% in the first half of the year. Strong growth in new housing (both public and private) up by 27% and in private industrial (up by 20%) was offset by weakness in infrastructure and related public sector projects. For the year as a whole we expect growth of 4.6% slightly down on the June forecast of 5.1%. UK Trade Figures … The trade deficit (goods) increased to £10.2 billion in July offset by a £6.8 surplus in services. Our forecasts for the year as whole - unchanged as a result. We expect the deficit (trade in goods) to be £30.8 billion in the quarter and £112.5 billion for the year as a whole. Is this a threat to recovery? Not really. The trade in services surplus will reduce the combined deficit in the year, to around £30 billion. Less than 2% of GDP, the deficit is easily funded. No pressure on policy makers to increase rates, assuming overseas dividends recover to finance the shortfall. Growth in the UK … Despite the soft figures in manufacturing and construction in July, our forecast for growth in the UK in the Q3 and for the year as a whole remains unchanged around 3.1% So what of base rates … Last week, base rates were held at 50 basis points. The chances of a rate rise before the end of the year are receding. Next week’s inflation and retail figures will be soft but the labour stats will suggest further tightening in the claimant count and vacancy rates. There will be nothing in next week’s data to precipitate a rate rise this year. So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling fell against the dollar to $1.626 from $1.630 and down against the Euro at 1.254 from 1.259. The Euro was up against the dollar at 1.297 (1.295). Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $97.62 from 100.98. The average price in September last year was $111.60. Markets, move down slightly. The Dow closed down at 16,978 from 17,103 and the FTSE closed down at 6,806 from 6,855. UK Ten year gilt yields move up to 2.55 from 2.49 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.60 from 2.44. Gold was further tarnished at $1,227 from $1,265. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Economics, Strategy and Social Media ... Experience worth sharing. Disclaimer The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. If you do not wish to receive any further Saturday Economist updates, please unsubscribe using the buttons below or drop me an email at [email protected]. If you enjoy the content, why not forward to a colleague or friend. Or they can sign up here
0 Comments
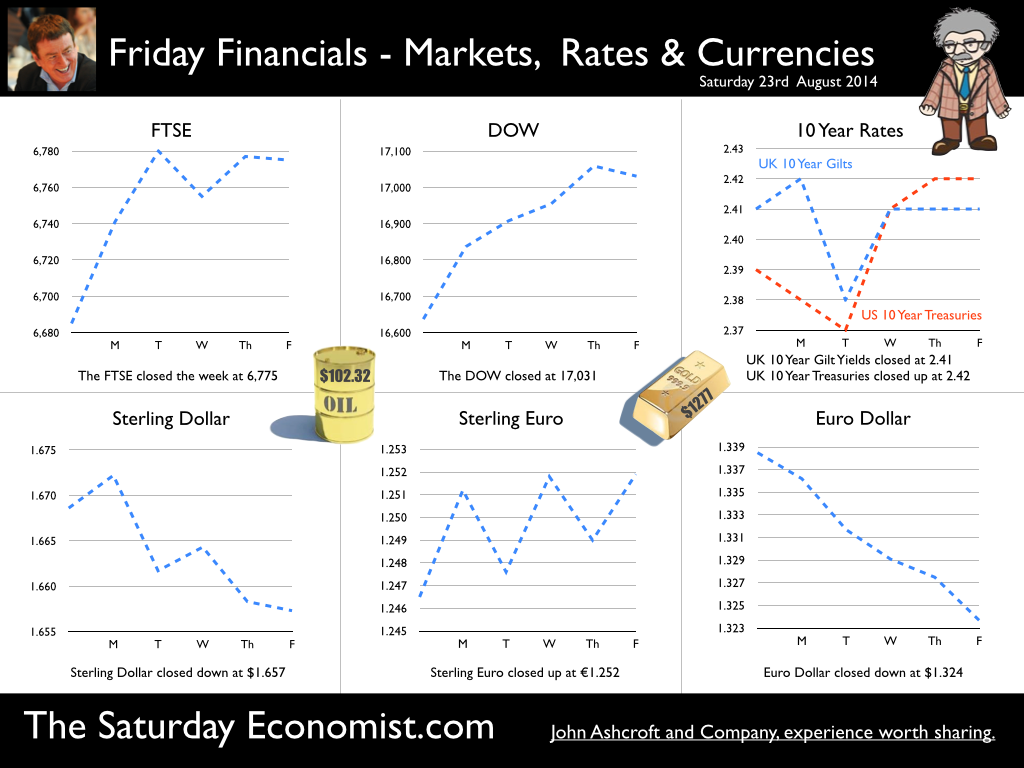
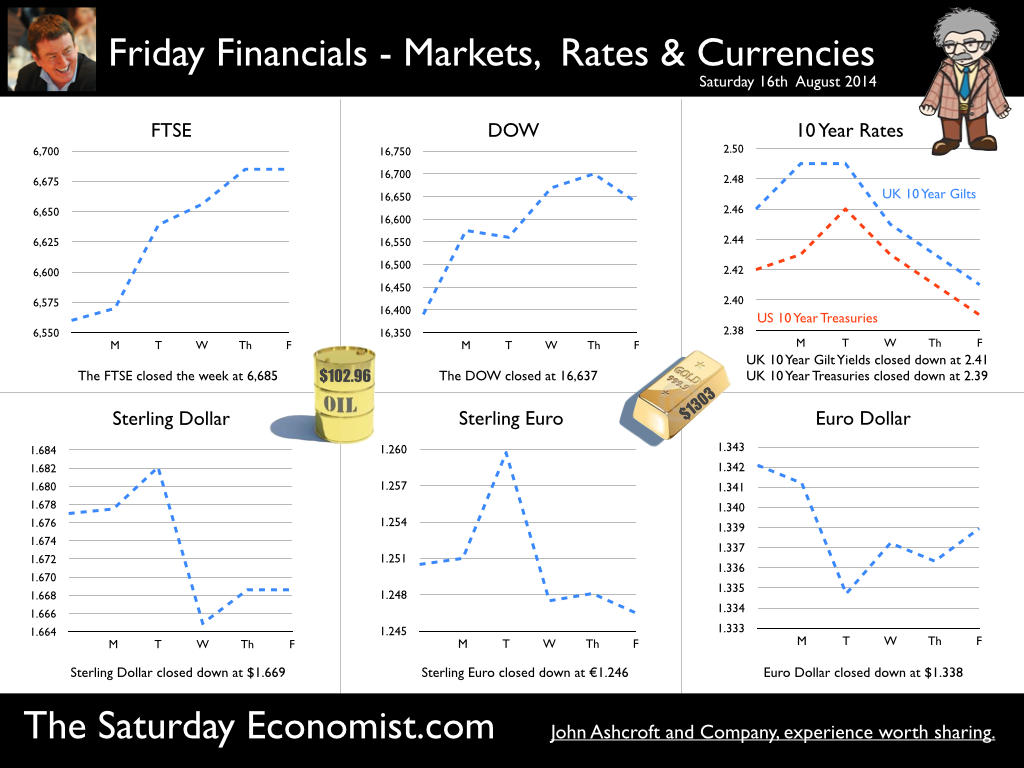
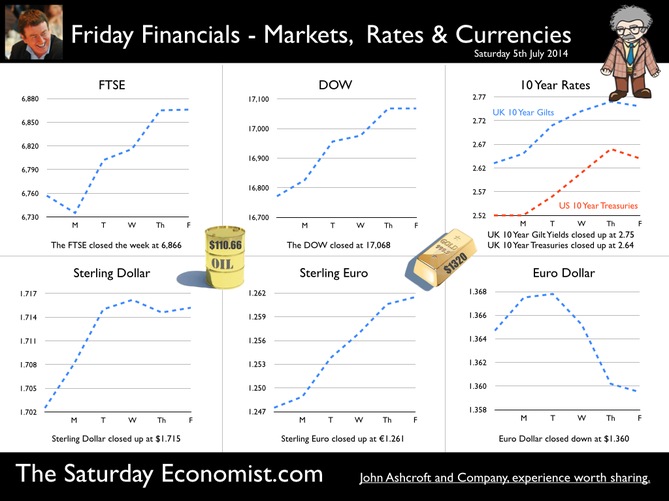
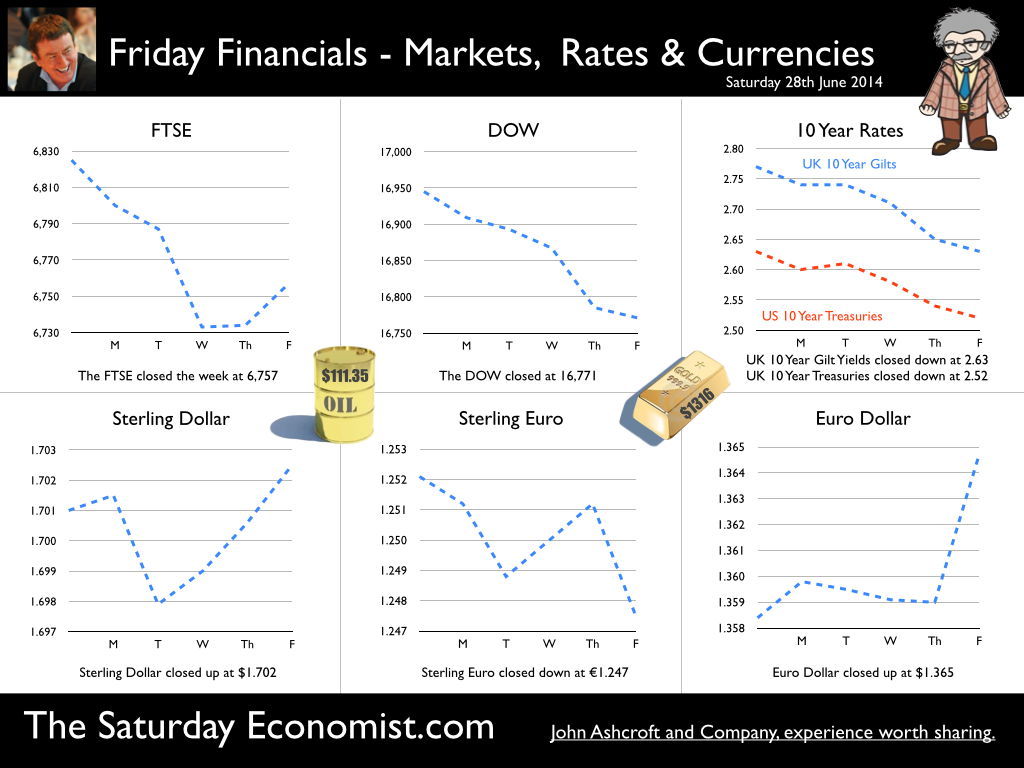
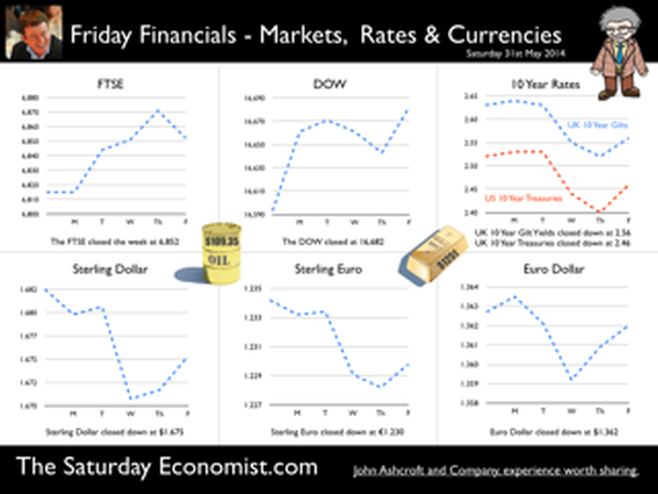
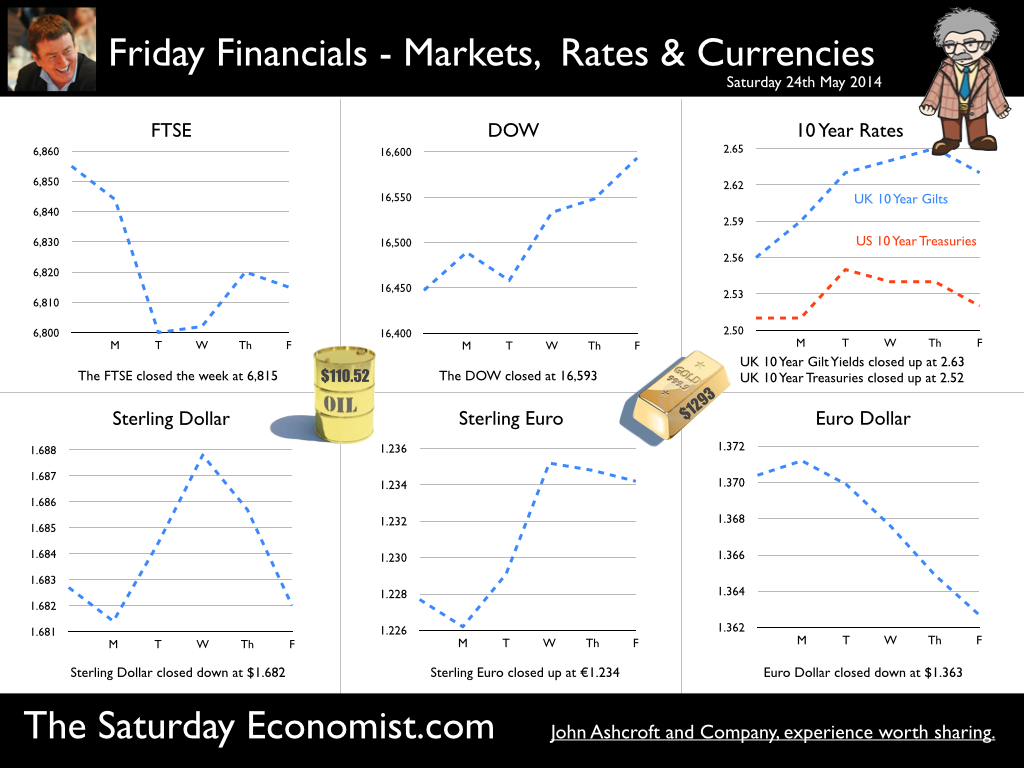
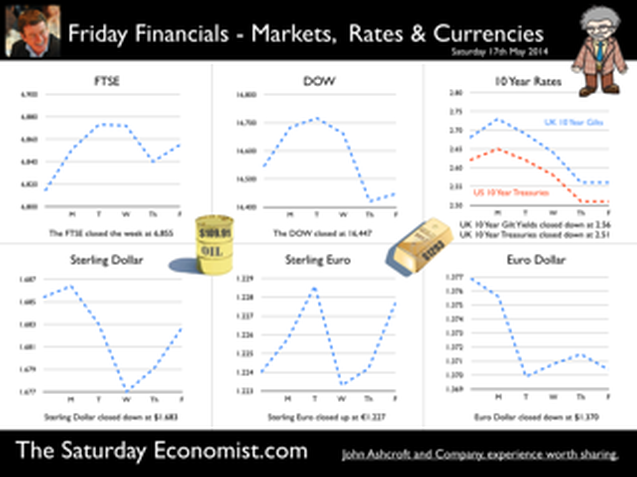
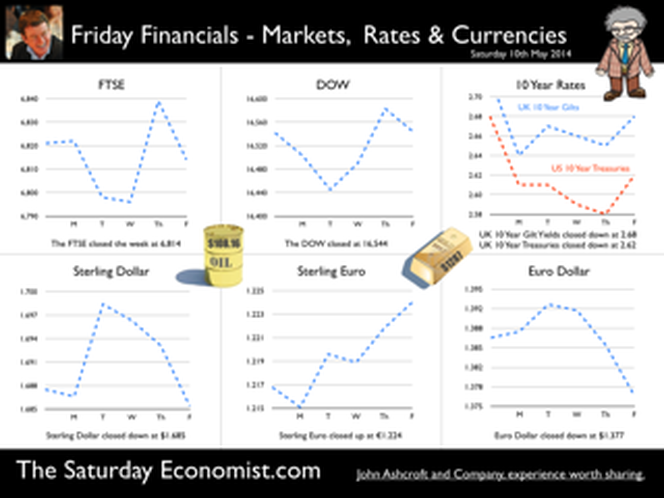
 Jackson Hole, Wyoming. Skiing in Winter and Fly Fishing in Summer, there are several perks to the role of central banker. This week the bankers were in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, fishing for answers to the employment - inflation conundrum. The occasion - the Federal Reserve, Kansas City, Economic Symposium, Jackson Hole, Wyoming. Why Wyoming? You may well ask? In 1982 the conference moved to Jackson Hole (Kansas City district) to persuade Paul Volcker, then chairman of the Fed and an avid fly-fisherman, to attend. Flies and fish were the big lure for the head of the Fed - and so it began. The location, based some 2,000 miles from New York and 5,000 miles from London is not ideal. Communication - in the early days - not always ideal either. Want a copy of the New York Times? The local store stocked today’s and yesterday’s but if you wanted today’s copy, you had to come back tomorrow - delivery lagged a day behind. Monetary Policy and the Muddler Minnow* … This year the theme was Labor Market Dynamics and Monetary Policy. Mario Draghi reassured markets there would be no early rise in rates in Europe! Quelle Surprise! Janet Yellen delivered a lecture on structural, cyclical, secular and frictional unemployment before claiming the mantle of Truman’s two handed economist to explain the Fed’s stance on future monetary policy. On the one hand … “If progress in the labor market continues to be more rapid than anticipated or if inflation moves up more rapidly than anticipated, resulting in faster convergence toward our dual objectives, then increases in the federal funds rate target could come sooner than the Committee currently expects and could be more rapid thereafter.” On the other hand … “If economic performance turns out to be disappointing and progress toward our goals proceeds more slowly than we expect, then the future path of interest rates likely would be more accommodative than we currently anticipate.” Excellent. Yellen then left the room, thrust on a pair of waders, tied on a muddler minnow before making an excellent double spey cast into the River Snake. [*The muddler minnow is currently one of the most favoured trout flies amongst central bankers.] The MPC Minutes … muddying the waters … Back in the UK, the Bank of England released the minutes of the August MPC meeting. Two members of the committee, Martin Weale and Ian McCafferty voted for an increase in base rates by 25 basis points. The Carney consensus has cracked. Charm school is out for the Summer. Markets fell, Sterling rallied, on the prospect of an early rate rise. Inflation Update ... The day before, the ONS released the inflation figures for July. CPI fell to 1.6% from 1.9% prior month. Markets had rallied, Sterling fell, prospects of an imminent rate rise postponed. No one seemed to notice that service sector inflation was unchanged at 2.5%. The overall drop in the headline rate - attributable to goods inflation down to 0.8% from 1.4% in June. So why the drop in goods inflation? Manufacturing output prices were flat but input costs fell by over 7% in the month. Effects of sluggish world trade, weak commodity and energy prices were exacerbated by the translation impact of a stronger Sterling. Government Borrowing … Thursday and the ONS released figures on government borrowing for the month of July. Four months into the year and borrowing remains off track compared to last year and to plan. In the first four months, total borrowing was £37.0 billion compared to £35.2 billion in 2013. In July borrowing was down to £0.7 billion from £1.6 billion last year. An improvement but with an economy expanding by over 3% in the first half of the year, we would expect a big improvement in borrowing given the strength of the recovery. Government spending is not the problem, nor VAT receipts up by 5%. The problem is revenues from income and capital gains tax are actually down on prior year over the first four months of the fiscal year. In part this is a result of strong receipts in the first quarter last year which may level out in due course. Compared to two years ago, revenues are up 5%. Even so, for the year as a whole the Chancellor will still have some work to do if the OBR target is to be met. Retail Sales … Retail sales in July were up by 2.6% after growth of 4% in the first half of the year. A disappointment, perhaps. Internet sales were up by 11% accounting for 11% of all retail activity. It will take more than a few digital mannequins to reverse fortunes on the high street but it is a tad to soon to make the call about a slow down in overall activity. The house market remains strong in terms of prices and the Council of Mortgage Lenders reported a 15% increase in gross mortgage leading last month. So what of base rates … The MPC minutes suggested the rate rise could come earlier than expected but news on inflation and retail sales suggest the rates will be kept on hold until 2015. No rate rise in prospect in Europe but Janet Yellen has “nowcast” a muddler minnow into the thought stream. A rate rise in the USA on the cards for Q2 next year or even earlier? Possibly. In the UK - February or June would appear to be the call. So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed down against the dollar at $1.657 from $1.669 but up against the Euro at 1.252 from 1.246. The Euro was down against the dollar at 1.324 (1.246). Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $102.32 from 102.96. The average price in August last year was $111.28. Markets, rallied on the fishing report from Wyoming. The Dow closed up at 17,031 from 16,637 and the FTSE closed up at 6,775 from 6,685. UK Ten year gilt yields were unchanged at 2.41 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.342 from 2.39. Gold was largely unchanged at $1,302. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Economics, Corporate Strategy and Social Media ... Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  The Inflation Report Press Conference … Reassurance from the Inflation Report Press Conference this week. The Bank of England may be uncertain about what is happening in the economy but it is certainly not clueless. Excellent. £3.5 million spent on the economics model and 200 PhDs in the pot to stir up the data, not all is for nought. James Macintosh of the FT put the difficult question “It would appear you've been moving over the past five years from a fair degree of certainty towards a fair degree of cluelessness and currently - you are at the more clueless end of the spectrum.” Is this a fair point? Well perhaps. Larry Elliott of the Guardian had begun the challenge suggesting there's a wide range of views on the Committee about the likely degree of slack in the economy. There is uncertainty about the housing market, wages may go up, they may not go up. Guidance on the pace and extent of interest rate rises is an expectation not a promise … “I mean once you cut through all this doesn't it lead you to three conclusions - one, that the Bank hasn't really got a clue what's going on out there; two, that the MPC is divided about what's going on out there; and thirdly, any person thinking about taking out a mortgage on the basis of the Bank's forward guidance would be ill-advised to do so, because anything you say, has to be taken with a very large pinch of salt?” Oh dear ... The Carney honeymoon is over … Well one thing we can be certain about, this is not the questioning we would have expected under Governor King. For Governor Carney the honeymoon is over. So much for the open routine. The Emperor’s economics models are proving to be as insubstantial as the clothing. Perhaps it is time to return to the enigmatic, grumpy old professor emeritus routine, dismissive of those of a lower intellectual order including undergraduates and the press core particularly. Ed Conway now with Sky News, would occasionally rattle Governor King teasing about the accuracy of the inflation forecasts, (not actually forecasts of course) but Governor Carney,cast in the role as the unreliable boyfriend, is taking more and more hits. All a bit of a muddle … Clearly Asa Bennett From the Huffington Post rattled the Governor, sensitive to criticism of forward guidance, “I just wanted to ask Governor about the evolution of your forward guidance plan, particularly when it started with the sort of clear to understand unemployment threshold, and then the sort of output gap, and then this bolt on about pay growth. Do you wish you started with this at the beginning? Hasn’t it all been a bit of a muddle or is it a learning process? “Well you’re muddled I'm afraid”. The playground retort from the Governor of the Bank of England. So is that the best we can get? The Old Lady of Threadneedle Street - the Aunt Sally of Fleet Street … The Old Lady of Threadneedle Street is becoming the Aunt Sally of Fleet Street. It would help if Jenny Scott, Executive Director of Communications, chairing the press conference, appeared to know some of the names of the press corp, instead of jabbing a pencil in this or that direction, when it came to question time. Perhaps Jenny was trying to ward off evil spirits, waving the magic wand of oblivion, which Governor King carried so successfully in his cloak. For debutante MPC member Minouche Shafik, it was all too much. Shifting uneasily, apparently bored, struggling under the weight, not of office but of a voluminous hair style, the governor allowed Minouche one question response on Europe … Minouche : “It would be good for us if Europe grew faster since it’s our key trading market, but for the near term that doesn’t look very likely”. “That’s all we have time for”, said the Director of Communications and that was that. Well, we must hope there is much more to come. So what happened this week? GDP Estimate … The ONS second estimate of GDP was released this week. Growth in the UK Q2 increased by 3.2% compared to the prior estimate of 3.1%. Actually the numbers hadn’t changed, the statisticians were using a more accurate calculator this time round for the rounding. Our estimates of growth for the year are unchanged at 3% which makes the Bank of England estimates of growth (3.5%) all the more difficult to understand. Either the economy will grow at an eye watering 4% in the second half of the year or the Bank expects big revisions to the data in September as a result of the inclusion of drugs and prostitution in the national accounts. Who would have thought hookers had that much clout. We shall have to wait until the end of September for the update. Labour Market Stats … The jobs outlook just gets better. The claimant count rate fell to 3% in July at just over 1 million unemployed. 400,000 have found work in the past year. At the current rate of growth we will be closing the job centres at the end of 2016, there will be no on left on the register looking for work. The wider LFS data confirmed the trend with the unemployment rate falling to 6.4%. More people in work, unemployment rates falling, recruitment increasing, skills shortages heightening, which makes the pay data even more inexplicable. Earnings increased by less than one per cent in June. We would expect increases in line with inflation or more at 3% plus at this stage in the recovery. For this we have much sympathy with the models at the Bank of England, something strange is happening on Planet ZIRP. Maybe low rates are the problem and no the solution? So what of base rates … Growth and jobs data would push the argument for a rates rise before the end of the year. Inflation and pay data would suggest the rates could be kept on hold until 2015. The latest data from Europe confirms a rate rise is off the agenda for months if not years to come. The MPC will be loathe to act ahead of the Fed and not too eager to move in advance of the ECB. Markets assumed rates will be kept on hold as a result of the Inflation Report… So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed down against the dollar at $1.669 from $1.6774 and down against the Euro at 1.246 from 1.252. The Euro was down against the dollar at 1.246 (1.341). Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $102.96 from 105.02. The average price in August last year was $111.28. Markets, rallied on the rates news. The Dow closed up at 16,637 from 16,554 and the FTSE closed up at 6,685 from 6,567. UK Ten year gilt yields were down at 2.41 from 2.55 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.39 from 2.49. Gold was largely unchanged at $1,303 from $1,305. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. 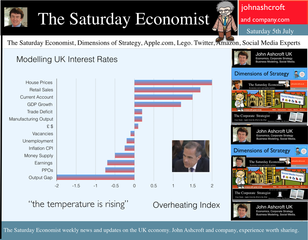 I made a trip to Liverpool this week. It was the Battle of the Economists, part of the International Festival of Business programme. Eight top economists were “in the ring” swapping punches. I “refereed” the morning event and hosted the Question Time session. It was a great event in the IFB calendar with lots of interesting perspectives on the world and UK economy. No blood spilled, nor egos bruised the outcome! To close the session, I asked the panel for views on when UK interest rates would begin to rise. Some argued for an immediate rate rise, most expected rates to rise in February next year and a few expected rates to rise in the November this year. As we said last week, “It is true there have been a lot of conflicting signals about when rates will rise! Following Mark Carney’s Mansion House speech, the odds in favour of a rate rise before the end of the year increased but then lengthened slightly, on the low inflation figures for May and the strength of sterling ”. “Don’t watch my lips - watch the data!” the new forward guidance from the Governor. This week, the data continued to suggest the rate rise would be sooner rather than later. House prices up almost 12% … House prices increased by almost 12% in the year to June according to Nationwide. In London prices increased by 26%. The price of a typical property in London, reached the £400,000 level with prices 30% above the 2007 highs. Should we be concerned? Of course but the rate of increase in house prices of itself, will not lead to an increase in interest rates necessarily. Sir Jon Cunliffe, Deputy Governor for Financial Stability at the Bank of England was in Liverpool this week. “The main risk we see arising from the housing market is the risk that house prices continue to grow strongly and faster than earnings. The concern is the increase in prices leads to higher and more concentrated household indebtedness.” The Bank is not worried about the rise in house prices per se. The FPC (Financial Policy Committee) is concerned about the risk to the banking sector from high household indebtedness exposed to the inevitable rate rise and potential collapse in asset prices. The introduction of measures on interest rate multiples and leverage, the confines of policy intervention for the moment. Car Sales up 10.6% year to date … The strength of the housing market demonstrates the strength of consumer confidence and spending. The economy is growing at 3% this year, retail sales were up by almost 4.5% in the first five months of the year, car sales were up by 6% in June and by 11% in the first six months. We are forecasting registrations will be over 2.4 million in 2014, higher than the pre recession levels recorded in 2007, placing additional pressure on the balance of payments in the process. Yet rates remain pegged at 0.5%! Does this continue to make sense? PMI Markit Purchasing Managers’ Index® Survey Data The influential PMI Markit surveys continue to demonstrate strong growth in the economy into June. In manufacturing, strong growth of output, new orders and jobs completed a robust second quarter. In construction, output growth continued at a four-month high and job creation continued at a record pace. In the service sector, the Business Activity Index, recorded 57.7 in June. The survey produced a record increase in employment with reports of higher wages pushing up operating costs. The Manchester Index™- nowcasting the UK economy The Manchester Index™, developed from the GM Chamber of Commerce Quarterly Economic Survey, slowed slightly from 35.1 in the first quarter to 33.6 in the second quarter, still well above pre recession levels. The data within the survey, confirms our projections for growth in the UK economy this year of 3%, moderating slightly to 2.8% in 2015. So when will rates rise ? The Saturday Economist Overheating Index revealed ... At the GM Chamber of Commerce Quarterly Economics Survey yesterday, we revealed the “overheating Index”. This is a summary of fourteen key indicators which form the basis of any decision to increase rates by the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC). The strength of consumer spending, reflected in house prices, retail sales and car sales would argue in favour of a rate rise earlier rather than later, as would the growth in the UK economy at 3% above trend rate. On the other hand, inflation, reflected in retail prices and manufacturing prices remain subdued. Despite the strength of the jobs market, earnings remain below trend levels. The decision, on when to increase rates, remains finely balanced for MPC members at this time. Our overheating index is broadly neutral but tipped slightly in favour of a rate rise now. By the final quarter of the year, assuming earnings and inflation rally from current levels, the decision will be much more clear cut. Based on data from the Overheating Index, we expect rates to rise before the end of the year. Clearly markets think so too ... So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed up again against the dollar at $1.715 from $1.702 and up against the Euro to 1.261 from (1.247). The Euro moved down against the dollar at 1.360 from 1.365. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $110.66 from $111.35. The average price in June last year was $102.92. Markets, US closed up on the strong jobs data. The Dow closed above the 17,000 level at 17,068 from 16,771 and the FTSE was also up at 6,866 from 6,757, the move above 7,000, too much for the moment. UK Ten year gilt yields were up at 2.75 from 2.63 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.64 from 2.63. Gold was up slightly at $1,320 from $1,316. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. The Manchester Index™ The influential Manchester Index™, is developed from the GM Chamber of Commerce Quarterly Economic Survey. It is a big survey which is comprehensive, authoritative and timely. Now we also have the Manchester Index™. The Manchester Index™ is an early indicator of trends in both the Manchester and the UK economy. Using the Manchester Index we are in a great position to “nowcast” the UK economy and get a pretty good steer on employment and investment in the process.  The Governor was in front of the Treasury Select Committee this week. Pat McFadden raised a laugh about forward Guidance - “The bank is behaving like an unreliable boyfriend, one day hot, one day cold, - people on the other side of the message not really knowing where they stand”. But is that really fair? It is true there have been a lot of conflicting signals about when rates will rise! Following Mark Carney’s Mansion House speech, the odds in favour of a rate rise before the end of the year increased but then lengthened slightly, on the strength of sterling and the low inflation figures for May. The Governor is advising markets, “forward guidance is state contingent”. As the state of the economy changes, the timing of future rate increases will also change. No need to wait for the Quarterly Inflation Report to mark the move. The situation is fluid and dynamic. As the data changes, so will future rate rise probabilities. “Don’t watch my lips - watch the data!” the new guidance. Revisions to GDP data … And so it was, the UK data changed, slightly, this week with the revisions to growth in the first quarter. The ONS revised down growth in Q1 from 3.1% to 3%! This is hardly likely to impact on monetary policy in any way shape or form. The adjustments reflect minor statistical adjustments rather than major structural moves. Our forecast of growth for 3% in 2014 is unaffected by the change. Investment grabbed the headlines, increasing by almost 10% in the quarter. The year on year comparison was against a particularly weak quarter last year. We expect investment growth of over 7% for the year as a whole, using research data derived from the Manchester Index™. [GM Chamber of Commerce research data - capacity and investment intentions]. In the USA, the revisions to GDP growth in the first quarter were much more significant. The headlines confirm growth fell by 2.9% quarter on quarter. Yet, the underlying growth year on year was up by 1.5%. The FOMC expect US growth of 2.2% this year rising to over 3% next. So what of Medium Term Rates … In the UK, the governor would have markets believe rates will rise slowly and thereafter are unlikely to rise above 2.5% in the medium term. In the USA, the Fed present no such illusion. Medium term rates, according to members of the FOMC, are expected to rise to 4% plus and some members expect this to occur by 2016. For now, US Bond traders believe the FOMC is too optimistic about the economy. Interest rates will remain low well into this decade. But if it does happen “over there”, is the UK - US spread manageable? Hardly likely. The medium term path of UK base rates is set to return to the 4.0% plus norm in due course, narrowing the divide. As for the timing - well that is another "guidance" issue altogether! So what happened to sterling ... The pound closed up against the dollar closing above the highly significant $1.70 level. Sterling closed at $1.702 from $1.70, slipping against the Euro to 1.247 (1.252). The Euro moved up against the dollar at 1.365 from 1.358. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $111.35 from $114.70 as Middle East concerns cleared slightly. The average price in June last year was $102.92. Markets, closed down. The Dow closed down at 16,771 from 16,945 and the FTSE was also down at 6,757 from 6,825. UK Ten year gilt yields were down at 2.63 from 2.77 and US Treasury yields closed unchanged at 2.63. Gold was steady at $1,316 from $1,314. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  The Governor of the Bank of England, was before the Treasury Select Committee this week. The members of the committee were disturbed. The MPC and the Governor in particular were behaving like an unreliable boyfriend, one day hot, one day cold, leaving "people" not really knowing where they stand! Is that entirely fair? We look to Shakespeare for advice on the "Quality of Guidance following the leader in The Times today. The quality of guidance is not strained, It droppeth as the gentle rain from heaven. Upon the market place beneath. It is thrice blest. It blesseth him that giveth and him that provides an update some months later. Tis mighty and moves markets, Yeah even the lofty dollar trembles at the sound. It becomes the governor of the Bank of England, yeah even better than the crown. His script doth amply demonstrate the force of monetary policy and power. The attribute to awe and majesty, wherein doth sit the mystery of spare capacity and yield. Guidance is a sceptred sway, first this way and that. Dethroned in the hearts of Kings long past, it is an attribute to deity itself. For monetary power doth then show likest best, when reality seasons theory and pragmatic policy rules the nest. Anon.  It may have taken some time but households across Britain have finally come to terms the with strength of the recovery. According to GfK, the UK Consumer Confidence Barometer increased to levels last seen in the early part of 2005. Rejoice - we are having a recovery - would have been the Conservative mantra under Prime Minister Thatcher. Confidence in the economic situation of the country, increased to the highest level EVER, since records released in 2004. The propensity to spend is back to levels of 2006, even though the financial situation of households index is still below pre recession numbers. No surprise, perhaps, but with interest rates at such low levels, there is no real uptick in the intentions to save - for the moment at least. Interest Rates set to rise … Maybe households are waiting for the rates to rise. According to Markit®, nearly one in four households expect a rate rise within the next six months … almost half expect rates to rise within the next twelve months. Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit® said, “the recent upbeat news-flow on the economy, strong economic growth in the first quarter, record employment growth and surging house prices, means an increasing number of people think it inevitable that policymakers will be forced into an earlier rate hike than previously envisaged.” Quite right! In fact almost ten per cent, think rates are set to rise within the next three months! So much for forward guidance from the Bank of England. Charlie Bean and Baby Steps … Charlie Bean, the outgoing (as in departing) deputy governor of the Bank of England has suggested “The argument for gradual rises suggests rates should start to go up sooner. The rise could start with “baby steps to avoid making mistakes”. “There’s a case for moving gradually because we won’t be quite certain about the impact of tightening the Bank rate, given everything that has happened to the economy.” The sentiment was also echoed by MPC member Martin Weale, this week. "We can wait a bit longer. How long that 'bit longer' will be I'm not sure.” Ah yes, the merits of forward guidance and a clear steer on monetary policy. Governor Carney will have to whip the MPC troops into line if we are to avoid complete confusion on the direction of rates. The Bank would still have us believe rates will rise in the second quarter of next year. UK rates should rise in the Autumn … In our Greater Manchester Chamber of Commerce Economic Quarterly Outlook, to be released next week, we begin to caution, UK rates should be on the rise in the Autumn, if the present trends in household spending, retail sales and the housing market continue. From an international perspective, the MPC will be reluctant to act ahead of the Fed and the ECB. In the first quarter, US GDP recorded growth of just 2% year on year, postponing, perhaps, the inevitable rate rise. In Europe, fears of deflation may force the ECB to act, to ease, rather than tighten, monetary conditions still further in the June meeting. Japan ends fears of deflation … In Japan, fears of deflation have been assuaged by Abenomics. The solution to fears of falling prices - increase the rate of sales tax and push up prices! Japanese inflation increased by over 3% in April, half of which is explained by the hike in taxes! Fears may later emerge about the slow down in growth, such is the Ground Hog day experience of the lost decade but for the moment, rejoice - the deflationary spiral has been broken in the East! Good News for growth in the UK … Good news for growth in the UK continued this week according to today’s Financial Times. Drugs and prostitution will add £10 billion to the UK economy. Yes, the news that prostitution and drugs will be included in the calculation of the National Accounts from September onwards, adding a new dimension to the “Service Sector” offer. The change will add almost £10 billion to the National Accounts. Hookers will contribute £5.3 billion to “output” (GDP(O)) and drug addicts will add £4.4 billion to the calculation of expenditure (GDP(E). According to ONS research, in 2009, 60,879 prostitutes serviced 25 clients per week at an average spend of £67.19. Don’t you just love economics! If only "tricks" paying 19p could be persuaded to spend more … that would be a recovery! So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed down against the dollar at $1.675 from $1.682 and down against the Euro at 1.230 (1.234). The dollar closed broadly unchanged at 1.362 from 1.363 against the euro and at 101.80 (101.97) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $109.35 from $110.52. The average price in May last year was $102.30. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,682 from 16,593 and the FTSE moved up to 6,852 from 6,815. The markets are set to move higher. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.56 (2.63) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.46 from 2.52. Gold moved down to $1,251 from $1,293. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. 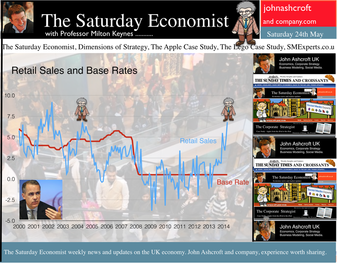 It was one of those heavy weeks for economics releases. Inflation, retail sales, government borrowing plus the eagerly awaited second estimate of GDP. Add in ONS house price information and a heady cocktail of excited headlines was to be expected from the financial pages. Inflation data as expected … It began quietly enough with the inflation data. No surprises, CPI inflation edged up to 1.8% in April from 1.6% in the prior month. The large rise in service sector inflation to 2.8% from 2.3% was offset by a small decline in goods inflation, falling to 0.9% from 1.0%. The uptick was marginally reflected in producer prices, increasing to 0.6% from 0.5%. The more volatile input costs, fell at a slower rate -5.5%, from -6.3% prior month. Energy and oil prices, were again significant in the reduced input costs. Imported metals, chemicals, parts and equipment fell significantly assisted by the 10% appreciation of sterling against the dollar. For the year as a whole, we think inflation will hover close to the target for the best part of the year. The risk remains to the upside in the final quarter. A rise in international prices, and domestic demand, boosted by compression in the labour market is likely to push prices higher. No risk of deflation on the UK horizon, a real risk to the upside is developing. House Prices .. UK house prices increased, according to the ONS data, by 8% in the twelve months to March. “The house market may derail the recovery", the headline. “Carney believes that house prices are the biggest risk to the economy” the great caution. No matter, that house prices increased by over 9% in the prior month or that house prices outside London are increasing by just 4% on average. In the North West prices increased by just over 3%, in Scotland prices hardly increased at all. In London, house prices increased by 17%. Foreign cash buyers at the top end of the market may be confusing the overall trend. However, significant volume and price escalation in the mid tier market is also impacting on price averages. Governor Carney has made it clear interest rates will not rise to combat rising house prices. The remit to action lies with the Financial Policy Committee. Already, action has already been taken to modify the Funding for Lending Scheme away from mortgage lending. Discussions between the Bank and Treasury will continue to consider modifications to the “Help to Buy Scheme”. Implementation of the Mortgage Market Review will also curb lending into 2014. There is a structural problem in the housing market. Mark Carney, Governor of Threadneedle Street, points out that Canada has half the population of the UK but builds twice as many houses. No wonder there is a supply issue. But is the Bank of England prepared to help out? Not really. The Little Old Lady will not turn a sod, grab a hod nor build a single house this year. “We are not in the business of building houses” the Governor’s mantra. The Bank of England will not build a single house in this cycle but neither will it allow the housing market to derail the recovery, provoking a premature move in base rates. Retail Sales … Retail sales figures, on the other hand, suggest rates may have to rise much sooner than expected. Retail sales volumes increased by 6.8% in April compared to prior year. It was May 2004 when retail sales volumes increased at a similar rate. Base rates were 4.75% at the time rising to over 5% within eighteen months. Retail sales values increased by just over 6%. Online sales increased by 13%, accounting for 11% of total action. Consumer confidence is back to the pre recession levels, car sales are up by 8% this year and retail sales are soaring. From a UK perspective, rates should be on the move by the Autumn of this year. The MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and the ECB. The international context suggests the rate rise may be delayed until the second quarter of 2015. Thereafter, for those who would argue the forward horizon has 2.5% cap, the retail sales figures and base rate history should provide a warning of surprises to come. GDP Second Estimate … No surprises in the second estimate of GDP release for Q1. No revisions. The UK economy grew by 3.1% boosted by an 8% surge in investment activity. Manufacturing and Construction increased by over 3% and 5% respectively. The economy is rebalancing … well a little bit! Our May Quarterly Economics Update on behalf of GM Chamber of Commerce is released next week. The outlook for the year remains broadly unchanged. We expect the UK economy to grow by around 3% this year and 2.8% in the following year. The surge in retail activity has been a surprise, as is the continued strength in employment. The outlook remains much the same. Growth up, inflation rising slightly, employment increasing and borrowing, despite the blip in April, set to fall. Just the trade figures will continue to disappoint as we have long pointed out. So what happened to sterling? The pound closed broadly unchanged against the dollar at $1.682 from $1.683 and up against the Euro at 1.234 (1.227). The dollar closed at 1.363 from 1.370 against the euro and at 101.97 (101.54) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up at $110.52 from $109.91. The average price in May last year was $102.3. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,593 from 16,447 but the FTSE adjusted to 6,815 from 6,855. The markets are set to move, the push before the summer rush perhaps. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.63 (2.56 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.52 from 2.51. Gold was unchanged at $1,293 from $1,293. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  The Bank of England Inflation Report - May - So when will rates rise? Q2 2015 still the best bet. The final whistle not for some time yet! The Bank of England Inflation Report was released this week. It was all so predictable. The Governor’s opening remarks explained, “The overall outlook for GDP growth and inflation in this report is little changed from February. The UK economy continues to perform strongly. Having increased by more than 3% in the past year, output is now close to regaining the pre-crisis level. 700,000 more people are in work than a year ago and inflation is below, but close to, the 2% target. And so it proved. The strong labour market performance continued into April. The claimant count rate fell by 25,000, to a rate of 3.3%. The wider LFS data (to March) also reflected the improvement with a fall in the overall rate to 6.8%. On current trends the job centres really will be closing in 2017! The MPC expectations are for growth to increase by 3.2% in the second quarter and by 3.4% for the year as a whole, with continued expansion in household spending. Spending will be supported by an increase in real wages as inflation remains close to target and earnings increase moderately, with a gradual improvement in productivity. The MPC obsession with spare capacity continues. “While there is a range of views on the Committee, the best collective judgement is the margin of spare capacity is around 1% to 1.5% of GDP.” Charlie Bean is not entirely convinced about the “fuzzy concept” of spare capacity. “There is a real danger of spurious precision and the pretence of knowledge in this area” said the Deputy Governor. Quite so. That and many others perhaps! Does spare capacity impact on inflation prospects? Not so much. International inflationary pressures are key to current price trends and for the moment remain subdued. “The global picture is consistent with muted external inflationary pressures which, coupled with sterling’s appreciation, will moderate CPI inflation in the near term” said the Governor. Inflation has fallen sharply since the Autumn and the outlook for inflation in the medium term remains benign. A benign inflation outlook which will avoid undue pressure, in the short term, to increase rates, despite the strong growth figures and the buoyant housing market. So what of rates? The strength of the recovery has moved the economy “closer to the point at which interest rates will have to rise”, the official statement. So when will rates rise? In February, the MPC were happy to attach some credence to the market view that rates would begin to rise in the second quarter of next year. If anything the view in May is slightly more “dovish” or certainly more obtuse. “Our guidance is giving businesses and households confidence that we won’t take risks with price stability, financial stability, or the incipient expansion. It will promote the recovery in business investment, productivity and real wages, that a sustained expansion demands.” Rates are still unlikely to move until the second quarter of next year, the implication. As we explained last week, the MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and the ECB. Forward guidance then lapsed into sporting analogy as the governor explained : “Securing the recovery is like making it through the qualifying rounds of the World Cup. That is an achievement but not the ultimate goal. The real tournament is just beginning and the prize is a strong, sustained and balanced expansion.” Yes the the Governor is laying out his team formation for the tournament ahead . “A flat back four with growth, inflation, unemployment and borrowing all heading in the right direction. Two strikers up front, household spending, with support to come from business investment. Some confusion in mid field from the housing market but no mention of exports and rebalancing. So expect the odd own goal from the trade performance, errant on the wing, as we move into the final stages of the competition. The Governor, for now, is not “taking away the punchbowl as the match gets going”. Far from it, you may continue to consume alcohol on the terraces, well into the final stages. Base rates are not expected to rise anytime soon. Q2 next year still the best bet. The final whistle will not be blown for some time yet.” So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed broadly unchanged against the dollar at $1.683 from $1.685 and up against the Euro at 1.227 (1.224). The dollar closed at 1.370 from 1.375 against the euro and at 101.54 (101.18) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up at $109.91 from $108.16. The average price in May last year was $102.3. Markets, the Dow closed down at 16,447 from 16,544 but the FTSE closed up at 6,855 from 6,821. The markets are set to move, the push before the summer rush. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.56 (2.68) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.51 from 2.62. Gold moved up slightly $1,293 from $1,287. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  UK … This week, the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee voted to maintain Bank Rate at 0.5%. The Committee also voted to maintain the stock of QE assets at £375 billion. No real surprise, UK rates are expected to remain on hold until the second quarter of 2015. For the moment, UK policy is relatively clear cut. USA … Over in the USA, matters became a little more diffuse. Tapering is expected to continue, concluding the asset purchase programme in September or October this year. But then what happens next? In March, Janet Yellen head of the Fed, gave a clear indication US rates would begin to rise within six months of the end of tapering. Markets reacted badly and the FOMC was minded to recant. This week, testifying before the Joint Economic Committee of the U.S. Congress, Chairman Kevin Brady pushed pushed Yellen for more clarity on when the FOMC would raise interest rates. The Fed chair would not be drawn on this occasion. “There is no mechanical formula for when that would occur” - the somewhat mechanical and evasive response. Oh yes, a month is a long time in the formulation of monetary policy. Europe … In Europe, Mario Draghi, President of the ECB, faced the opposite dilemma. With modest growth forecast for Euroland this year, inflation below target at less than 1% and a Euro strengthening against the dollar ($1.375), the Italian banker is under pressure to alleviate European monetary conditions still further. Playing for time, Draghi stated policy makers at the bank were comfortable with action in early June. Action awaits the “staff projections” for growth and inflation next month, before considering the next step. Draghi must hope forecasts are revised upwards. Having promised to “do what it takes” to stimulate growth, the President is clearly at a loss, as to what can be done next. A reduction in base rates to the zero floor would have little economic impact. Experimentation with negative rates is a high risk strategy. The move would thrill academic economists but cause trauma in the markets. This is no time for experimentation with central bank novelties. QE is muted as a possibility but with German and French long rates at 1.45% and 1.9%, there seems little cause to push rates lower. Ten year bond rates in Spain and Italy are this week trading within 25 basis points of UK gilts. MPC Dilemma … So here in a way is the dilemma for the MPC. The UK economy is growing at 3% a year, unemployment is falling at such a rate, we may have to close the job centres in 2017. Inflation is below target but as Mario Draghi pointed out this week, it is the weakness in international commodity prices, oil, energy and food, the real determinants of low inflation. Low inflationary pressure exacerbated or assisted by the rise in the Euro (and Sterling) against the Dollar. The UK is caught in the Dollar Euro vortex, with basic economics pushing monetary policy in opposing directions apparently. The MPC cannot move ahead of the Fed or much in advance of Europe for that matter without pushing Sterling still higher. Deflation the illusion - OECD World Forecasts This month the OECD forecast a recovery in world growth this year to 3.4% in 2014 and almost 4% in 2015. The Euro area is set to grow by 1.2% and 1.7% over the period. Euro inflation is set to rise above 1.2% next year. Commodity prices (base metals) are demonstrating a price basing action, Oil Brent Crude basis is trading ahead of last year. The international price profile can change quickly and dramatically. The threat of deflation - an illusion - which may quickly dissipate. A strong ECB president should do nothing. The US must accept rates will rise within six months of the end of tapering. This would leave the MPC free to begin the inevitable rate rise in the second quarter of next year. Want to here more, don’t miss the quarterly economics presentation on Wednesday at DWF next week. The multi media roadshow rolls on! So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed unchanged against the dollar at $1.685 from $1.687 and up against the Euro at 1.224 (1.217). The dollar closed at 1.375 from 1.377 against the euro and at 101.18 (102.23) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed at $108.16 from $108.50. The average price in May last year was $102.3. Markets, the Dow closed unchanged at 16,544 from 16,542 and the FTSE also closed up at 6,821 from 6,814. The markets are set to the move, the push before the rush. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.68 (2.72) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.62 from 2.72. Gold moved down $1,287 from $1,296. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. It's just for fun, what's not to like! Dr John Ashcroft is The Saturday Economist. |
The Saturday EconomistAuthorJohn Ashcroft publishes the Saturday Economist. Join the mailing list for updates on the UK and World Economy. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
| The Saturday Economist |
The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The presentation should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.
|
The Saturday Economist, weekly updates on the UK economy.
Sign Up Now! Stay Up To Date! | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed