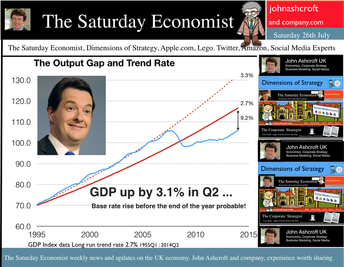
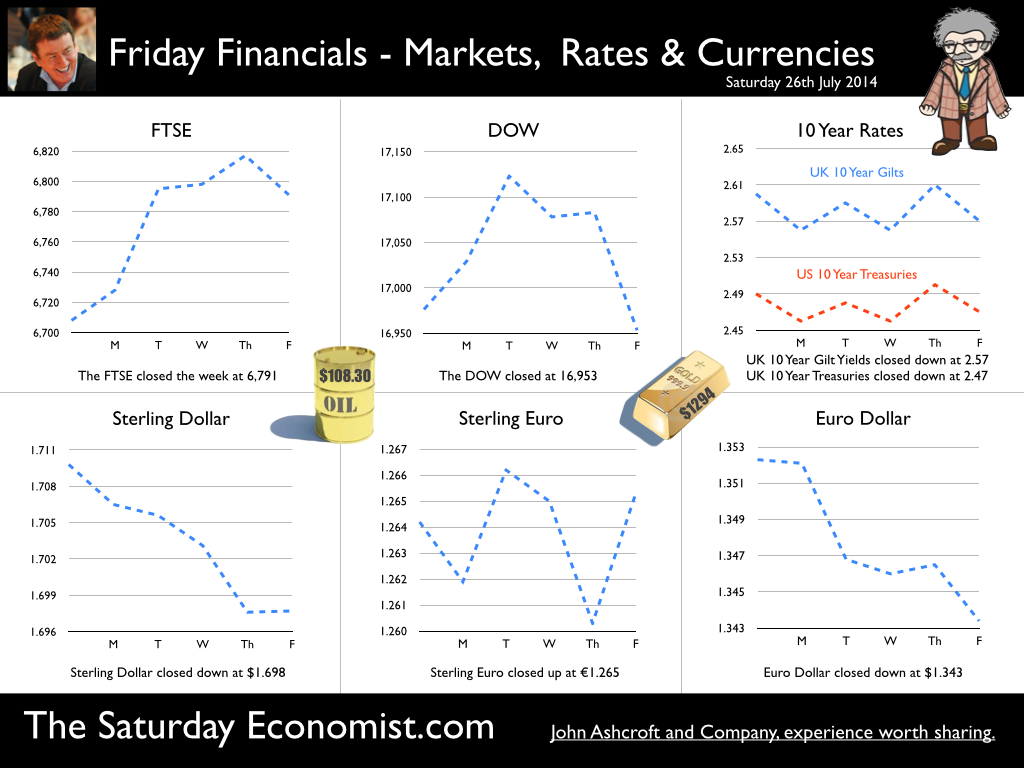
 GDP up by 3.1% in Q2 ... a rate rise before the end of the year seems probable! The UK economy grew by 3.1% in the second quarter of the year according to the latest figures from the ONS. The economy is on track for growth of just over 3.0% this year and 2.8% next. The output gap closed to 9.2% based on our estimated long term trend growth rate of 2.7%. Service sector continued to support the expansion (up by 3.3%) with particularly good performances in the leisure sector (4.9%) and business services sector (4.2%). Manufacturing and construction also made strong contributions with growth of 3.2% and 4.2% respectively. This is the first estimate of growth based on partial information. The next update is due on the 16th August. The initial estimate may well be revised up (3.2%) based on revisions to the manufacturing data. This week the IMF revised their forecasts of the UK economy to 3.2% for 2014 and 2.7% next. The UK will be the fastest growing economy in the western world with deleterious implications for the trade balance. If the IMF forecasts are correct, UK growth will accelerate in the second half of the year to 3.4%. It‘s simple arithmetic not complex economics! If that is the case, The Saturday Economist™ Overheating Index™ will move higher, bringing the prospect of a rate rise before the end of the year into clear focus. Retail Sales … Retail sales volumes increased by 3.6% in June 2014 compared with June last year. This is lower than the average over the first six months of the year, a period within which the volume of sales averaged 4.1%. (March and April were particularly strong months for retail activity.) Retail sales growth averaged 3.9% in our benchmark period [200Q1 - 2008Q1]. The performance in June of 3.6% suggests MPC members will rest easy on the news, with no pressure on a rate rise evident in the data. The amount spent online increased by 13.4% year on year, accounting for 11.3% of all retail spending. The pressure on conventional retail is continuing to increase significantly. UK Government Borrowing : No fiscal fizzle, the deficit is increasing! Writing in the New York Times this week, Paul Krugman talked of the imaginary US budget and debt crisis. Despite all the fears of deficit doomsters, the US federal deficit will be just 2.8% of GDP this year, down from 9.8% in 2009. The economy is growing and the deficit is falling. It's a fiscal fizzle. “We don’t have a debt crisis, and we never did”, says Krugman. Excellent news for them over there! But is it so good over here? According to the figures released by the ONS this week, in the first three months of the year, total borrowing was higher than first quarter last year by some £3 billion. Total borrowing was £36.1 billion compared to £33.6 billion last year. Despite economic growth in the quarter of over 3%, the deficit is increasing rather than falling. The government is off track to hit the deficit target of £95.5 billion in 2014/15. The deficit to GDP ratio was 6.5% in 2013/14 set to fall to around 5.5% this year. On current trends this is not about to happen. Total debt of £1.3 trillion has risen to over 77% of GDP. Analysts are beginning to call for more cuts in spending to resolve the problem. Yet spending over the first three months of the year was up by less than 1% [ANLP basis] assisted by a fall in interest costs of almost 3%. The problem for the Chancellor - Exchequer revenues actually fell. Despite an increase in the VAT take of just over 4%, Income and CG taxes were down by 3.5%, which is bizarre in an economy growing by 3% in real terms and over 5% in nominal values. The US economy invariably demonstrates an ability to rebound, evaporating the internal deficit in the process in quite dramatic fashion. Fiscal drag, generates a fiscal fizzle, vaporising the deficit and improving the outlook for the Fed. In the UK, the process is more protracted. The current trend is troubling. No need to panic just yet. We still expect a significant rebound in the tax take through the year as the economy continues to grow at over 5% in nominal terms. The deficit was revised down last year to £105.8 billion. The target of £95.5 billion appears to be a stretch for the moment. No fiscal fizzle for the Chancellor more like a slow burn - the OBR targets could still be hit! So what of interest rates … At the last meeting of the MPC, the Committee agreed that no increase in base rates was warranted. For some members the decision had become “more balanced in the past few months compared to earlier in the year”. The latest figures on retail spending and GDP would suggest the decision remains finely balanced but the hawks will be flapping their wings. The Saturday Economist™ Overheating Index™, ticked higher this week as a result of the GDP data. The chances of a rate rise before the end of the year edged higher in line with the index. So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed down against the Dollar at $1.698 from $1.709 but up against the Euro to 1.265 from (1.263). The Euro moved down against the dollar at 1.343 from 1.352. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $108.30 from 108.40 from. The average price in July last year was $102.92. Markets, closed up. The Dow closed below the 17,000 level at 16,953 from 17,100 and the FTSE was up at 6,791 from 6,749. UK Ten year gilt yields were down at 2.57 from 2.60 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.47 from 2.49. Gold was down at $1,294 from $1,310. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.
0 Comments
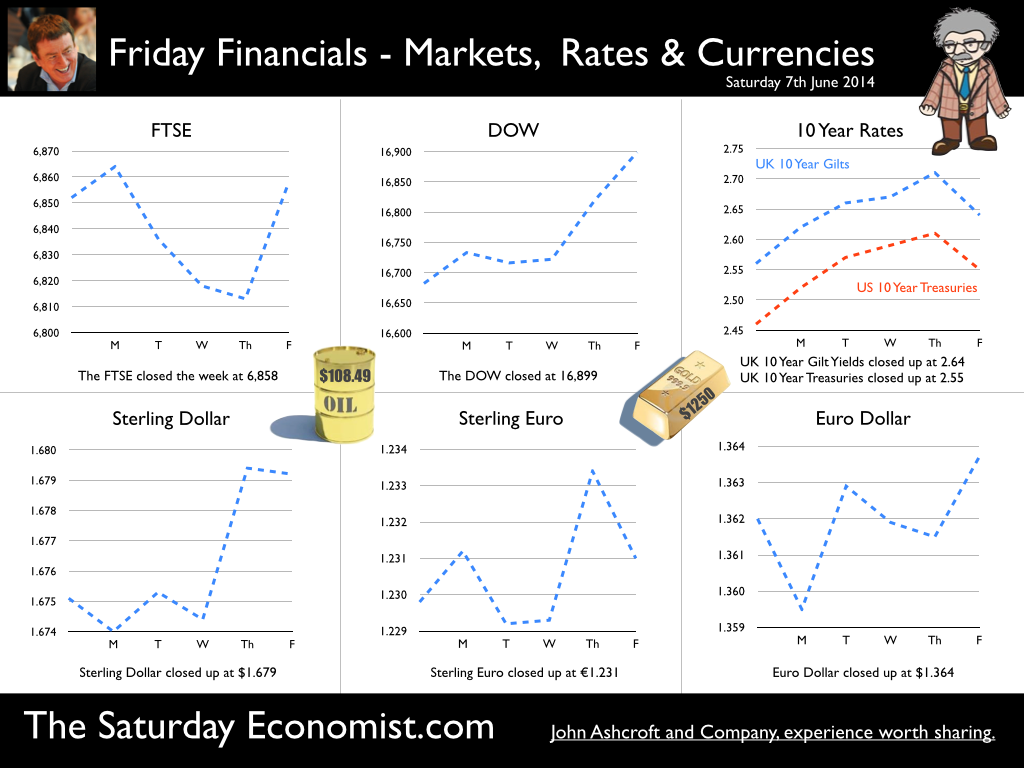
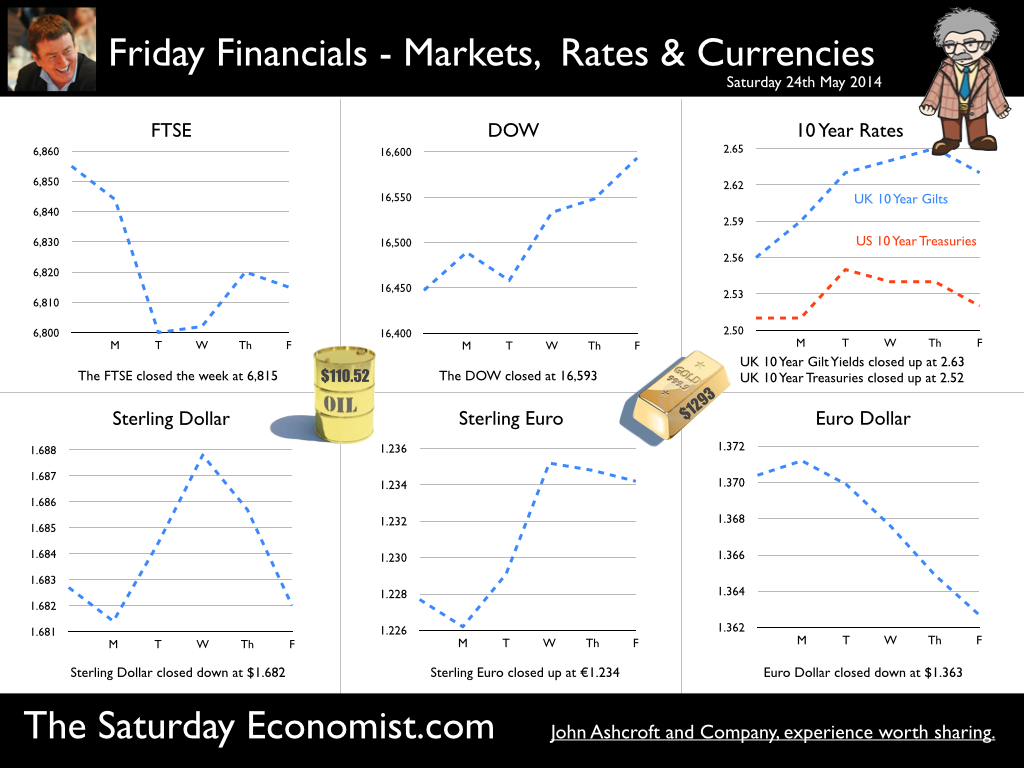
 The MPC left rates on hold this week. We will have to wait a few weeks to find out if the vote was unanimous. For the moment the consensus view is likely to have held. But for how long will this be the case? Forward Guidance is already becoming confused by statements from Martin Weale and Charlie Bean. By the Autumn, the Bank may adopt Dr Doolittle’s pushmi.pullyu animal as a mascot. So thin - the margin of spare capacity - for consensus. The timing of rates is likely to become more polarised amongst MPC members. Who will make the first move? The “Wad is on Weale” to be the first to break ranks. UK data suggest rates may rise sooner … The UK data continues to suggest rates may have to rise sooner than forward guidance implies. Car sales in of May were up by almost 8% in the month and by 12% in the year to date. According to Nationwide, house prices increased by 11% in the twelve months to May. The Halifax House Price data suggested house prices increased by almost 9% over the same period. According to Stephen Noakes, Halifax Mortgages Director : “Housing demand is very strong and continues to be supported by a strengthening economic recovery. Consumer confidence is being boosted by a rapidly improving labour market and low interest rates”. Christine Lagarde and the IMF squad were in the UK this week. The IMF has warned that house prices pose the greatest threat to the UK recovery. It called on the Bank of England to enact policy measures "early and gradually" to avoid a housing bubble. The Fund's annual health check, suggested the UK economy has "rebounded strongly” confirming growth would "remain strong this year at 2.9%”. The IMF also suggested growth is becoming “more balanced” but … Trade deficit deteriorates … There was no evidence of rebalancing in the trade figures for April. The trade deficit in goods increased to £2.5 billion in the month as the deficit (trade in goods) increased to almost £10 billion. OK, someone forget to include all the oil data in the month, which may have under stated exports by £700 million but this is a minor detail. We expect the deficit (trade in goods) to be between £112 billion and £115 billion offset by a £50 billion service sector surplus this year. No rebalancing on the trade agenda, as we have long explained. Markit/CIPS UK PMI® Survey Data The Markit/CIPS UK PMI® survey data was also released this week. “The UK manufacturing upsurge continued”. The Manufacturing PMI index was 57.0 in May, down slightly from 57.3 in April. The survey noted strong growth in output and new orders. There was also a sharp rise in construction output. House building remained the strongest performing area of activity. The headline index was signaling growth for the thirteenth successive month at 60.0, compared to 60.8 prior month. The headline service sector index continued in positive territory at 58.6 compared to 58.7 last month. Service sector employment growth increased at the fastest rate in 17 years. Interest rate outlook … The strong growth in consumer spending, retail sales, car sales and the housing market continues. The outlook for output remains strong in construction, manufacturing and the service sector. We expect investment activity to increase this year. The unemployment rate will continue to fall, placing greater pressure on wage settlements, leading to an increase in earnings into the second half of the year. The trade deficit will continue to deteriorate albeit at a rate which is offset by the strength of the service sector surplus. Sterling will probably hold at current levels for the rest of the year. Inflation, will remain around target, such is the weakness of international energy and commodity prices for the near future. With such a strong outlook for the domestic economy, rates should probably be on the rise by the Autumn of this year. However the MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and the ECB. USA and Europe ... In the USA, Friday’s strong jobs report confirmed the economy is improving following the slight setback in the first quarter. Non farm payroll increased by over 200,000 as the unemployment rate held at 6.3%. For the year as a whole, the Fed may downgrade the growth forecast to around 2.7% from 3% currently. For the moment, forward guidance suggests US rates may begin to rise in the second quarter of 2015 but the outlook may be shortened, if the job trends continue. In Europe, the ECB is heading in another direction. The growth forecast within the Eurozone is just 1% this year but officials are concerned about the prospect of deflation. The latest HICP figure confirmed prices increased by just 0.5% compared to 0.7% prior month. The ECB decided to lower the interest rate on the main refinancing operations of the Eurosystem by 10 basis points to 0.15% and the rate on the marginal lending facility by 35 basis points to 0.40%. The rate on the deposit facility was lowered by 10 basis points to -0.10%. To support bank lending to households and business, excluding loans for house purchase, the ECB will be conducting a series of targeted longer-term refinancing operations (TLTROs) valued at €400 billion over a four year period. The scheme follows the success of the UK Funding for Lending Scheme. So what of forward guidance … Domestic considerations suggest UK rates should be on the rise towards the end of the year. For the moment, forward guidance in the UK and the USA suggests rates will be held until the second quarter of 2015. This may change, if the trends in job growth continue here and in the USA. In Europe, forward guidance is more concerned with the prospects of deflation and a “lost decade”. An increase in rates is not on the “horizon” nor even in the appendix. So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed up against the dollar at $1.679 from $1.675 and unchanged against the Euro at 1.231 (1.230). The dollar closed broadly unchanged at 1.364 from 1.362 against the euro and at 102.53 (101.80) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $108.48 from $109.35. The average price in June last year was $102.92. It is summer after all. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,899 from 16,682 and the FTSE moved up to 6,858 from 6,852. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.64 (2.56) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.55 from 2.46. Gold held at $1,250 from $1,251. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. 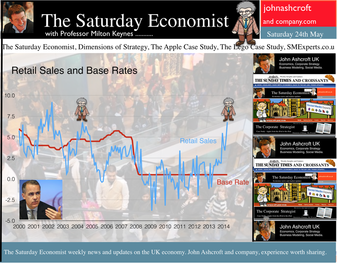 It was one of those heavy weeks for economics releases. Inflation, retail sales, government borrowing plus the eagerly awaited second estimate of GDP. Add in ONS house price information and a heady cocktail of excited headlines was to be expected from the financial pages. Inflation data as expected … It began quietly enough with the inflation data. No surprises, CPI inflation edged up to 1.8% in April from 1.6% in the prior month. The large rise in service sector inflation to 2.8% from 2.3% was offset by a small decline in goods inflation, falling to 0.9% from 1.0%. The uptick was marginally reflected in producer prices, increasing to 0.6% from 0.5%. The more volatile input costs, fell at a slower rate -5.5%, from -6.3% prior month. Energy and oil prices, were again significant in the reduced input costs. Imported metals, chemicals, parts and equipment fell significantly assisted by the 10% appreciation of sterling against the dollar. For the year as a whole, we think inflation will hover close to the target for the best part of the year. The risk remains to the upside in the final quarter. A rise in international prices, and domestic demand, boosted by compression in the labour market is likely to push prices higher. No risk of deflation on the UK horizon, a real risk to the upside is developing. House Prices .. UK house prices increased, according to the ONS data, by 8% in the twelve months to March. “The house market may derail the recovery", the headline. “Carney believes that house prices are the biggest risk to the economy” the great caution. No matter, that house prices increased by over 9% in the prior month or that house prices outside London are increasing by just 4% on average. In the North West prices increased by just over 3%, in Scotland prices hardly increased at all. In London, house prices increased by 17%. Foreign cash buyers at the top end of the market may be confusing the overall trend. However, significant volume and price escalation in the mid tier market is also impacting on price averages. Governor Carney has made it clear interest rates will not rise to combat rising house prices. The remit to action lies with the Financial Policy Committee. Already, action has already been taken to modify the Funding for Lending Scheme away from mortgage lending. Discussions between the Bank and Treasury will continue to consider modifications to the “Help to Buy Scheme”. Implementation of the Mortgage Market Review will also curb lending into 2014. There is a structural problem in the housing market. Mark Carney, Governor of Threadneedle Street, points out that Canada has half the population of the UK but builds twice as many houses. No wonder there is a supply issue. But is the Bank of England prepared to help out? Not really. The Little Old Lady will not turn a sod, grab a hod nor build a single house this year. “We are not in the business of building houses” the Governor’s mantra. The Bank of England will not build a single house in this cycle but neither will it allow the housing market to derail the recovery, provoking a premature move in base rates. Retail Sales … Retail sales figures, on the other hand, suggest rates may have to rise much sooner than expected. Retail sales volumes increased by 6.8% in April compared to prior year. It was May 2004 when retail sales volumes increased at a similar rate. Base rates were 4.75% at the time rising to over 5% within eighteen months. Retail sales values increased by just over 6%. Online sales increased by 13%, accounting for 11% of total action. Consumer confidence is back to the pre recession levels, car sales are up by 8% this year and retail sales are soaring. From a UK perspective, rates should be on the move by the Autumn of this year. The MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and the ECB. The international context suggests the rate rise may be delayed until the second quarter of 2015. Thereafter, for those who would argue the forward horizon has 2.5% cap, the retail sales figures and base rate history should provide a warning of surprises to come. GDP Second Estimate … No surprises in the second estimate of GDP release for Q1. No revisions. The UK economy grew by 3.1% boosted by an 8% surge in investment activity. Manufacturing and Construction increased by over 3% and 5% respectively. The economy is rebalancing … well a little bit! Our May Quarterly Economics Update on behalf of GM Chamber of Commerce is released next week. The outlook for the year remains broadly unchanged. We expect the UK economy to grow by around 3% this year and 2.8% in the following year. The surge in retail activity has been a surprise, as is the continued strength in employment. The outlook remains much the same. Growth up, inflation rising slightly, employment increasing and borrowing, despite the blip in April, set to fall. Just the trade figures will continue to disappoint as we have long pointed out. So what happened to sterling? The pound closed broadly unchanged against the dollar at $1.682 from $1.683 and up against the Euro at 1.234 (1.227). The dollar closed at 1.363 from 1.370 against the euro and at 101.97 (101.54) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up at $110.52 from $109.91. The average price in May last year was $102.3. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,593 from 16,447 but the FTSE adjusted to 6,815 from 6,855. The markets are set to move, the push before the summer rush perhaps. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.63 (2.56 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.52 from 2.51. Gold was unchanged at $1,293 from $1,293. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  “If inflation is the genie, deflation is the ogre that must be fought decisively...” Christine Lagarde head of the IMF was speaking to the National Press Club in Washington this week. With inflation below central bank targets in Japan, USA and Europe, the IMF believe the rising risks of deflation could prove disastrous for the world recovery. Western leaders, haunted by fears of the American Great Depression and Japan’s Lost Decade, are fearful of premature monetary tightening which could threaten the nascent recovery. In folklore, a genie is a supernatural creature who does the bidding once summoned. This may not have been the intentioned meaning by the boss of the IMF but Mark Carney Governor of the Bank of England, could be forgiven the interpretation. This week, the inflation figures for December were released by the ONS. CPI inflation increased by just 2%. For the first time in over four years, the genie returned to target, as would an obedient creature, undertaking the bidding of the new Governor of the Bank of England. The genie is working hard to obey. It has taken some time to get the message into the bottle and the genie back on message! Mission accomplished? With such success, it would be churlish to point out that in the same month, RPI increased from 2.6% to 2.7%, goods inflation actually went up and service sector inflation closed the year at 2.4%. For the moment the wild ride of the last four years has come to a close. As Christine Lagarde stated, “Optimism is in the air, the deep freeze is behind us and the horizon is much brighter.” In further good news, UK manufacturing prices increased by just 1% in December and input costs actually fell by just over 1%. Import prices of metals, parts and equipment fell, reflecting higher sterling values and lower world prices. For the moment, the inflation outlook for 2014 appears benign. Deflation is the ogre ... So what of ogres and deflation. Ogres are monsters in legends and fairy tales that eat humans and are particularly cruel, brutish or hideous. In the UK fears of deflation are not evident. We still expect inflation to hover slightly above target through the year. The ogre of deflation will be banished within the Kingdom. Particularly with earnings on the rise and a Chancellor of the Exchequer, as the handsome prince, up for re election, pledging an increase in the minimum wage to £7 an hour over the next couple of years. Inflation has fallen to target much faster than we had envisaged. The good news - as earnings rise, the boost to real incomes will lead to a sustained level of growth in consumer expenditure and retail sales. Higher but not quite as high as the latest UK data might suggest perhaps! Retail Sales the nymph spirit ... This week, the ONS released the retail sales figures for December. Sales volumes increased by 5.3% and values increased by 6.1% compared to December last year. Despite the fears of the major retailers, the consumer hit the high street with great gusto in the run up to Christmas allegedly. Internet sales, increased by 11.8% and small stores, experienced higher growth with sales increasing by just over 8%. Can retail sales have been so strong in December? Contractions in volume sales amongst food stores and petrols stations adds to the confused picture in the month. According to the ONS, in the three months prior to December, retail sales volumes averaged just 2%. So much for saving for Christmas. The surge in activity in December appears rather high and slightly at odds to the anecdotal evidence from retailers themselves. The BRC, British Retail Consortium suggests sales increased by just 1.8% in December as footfall actually fell. The BDO high street tracker reported sales down in the pre Christmas week with a recovery to 3.5% growth in the final week of the year. Debenhams, M & S, Morrisons and Sainsburys struggled in the Christmas period. Argos, Dixons, Halfords, Primark, Lidl and Ocado amongst the winners in the multi channel race. The 5% growth in volumes reported by the ONS appears to be a high call. So much for lies, damned lies and seasonal adjustment. Shrek shacking up with the Sleeping Beauty ... Ogres returned to the High Street this week as Sports Direct revealed a near 5% stake in Debenhams. Imagine Shrek shacking up with Sleeping Beauty, shudders must have swept around the Debenhams board room. The subsequent put and call option by Sports Direct, just added more confusion to the retail horizon. So what happened to sterling? The pound closed at £1.6422 against the dollar and 1.2127 against the Euro. The dollar closing at 1.3538 against the euro and 104.23 against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed at $106.48. The average price in January last year was almost $113, so no real threat to inflation from crude oil prices Markets, moved higher. The Dow closed at 16,458 and the FTSE closed at 6,829. 7,000 on the FTSE a soft call for the near term. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.84 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.82. Yields will test the 3% level as tapering accelerates into 2014. That’s all for this week. No Sunday Times and Croissants tomorrow or for the rest of this year for that matter. We are taking a break in this pre election year. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. The list is growing as is our research and our research team. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. |
The Saturday EconomistAuthorJohn Ashcroft publishes the Saturday Economist. Join the mailing list for updates on the UK and World Economy. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
| The Saturday Economist |
The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The presentation should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.
|
The Saturday Economist, weekly updates on the UK economy.
Sign Up Now! Stay Up To Date! | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed