Friday Forward Guidance ...
This is our Friday Forward Guidance for Friday 12th July. Every week we update our scenario forecasts for base rates in the U.S., UK and Europe over a three year period. We also include our expectations for inflation, as an input to the central bank reaction function, in the Saturday Economist updates.
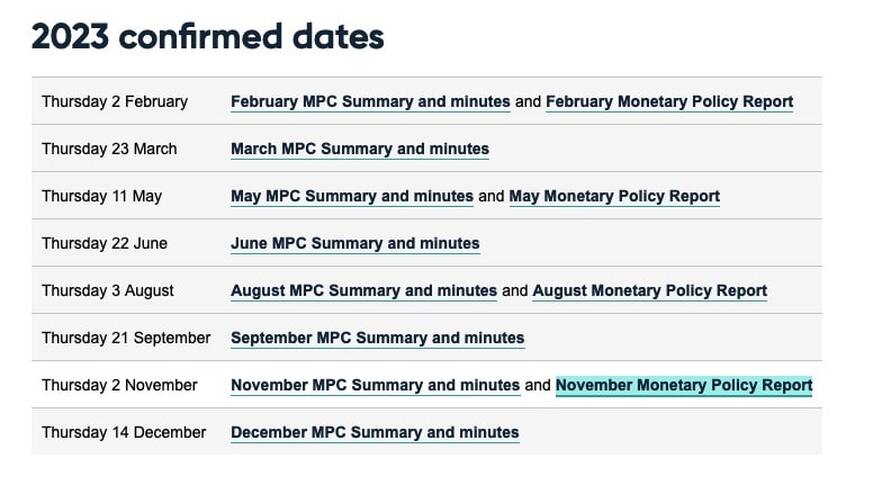
In latest central bank moves, the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) voted 7 to 2 in favour of maintaining the base rate at 5.25% for the seventh consecutive month. Monetary policy will need to remain restrictive for sufficiently long to return inflation to the 2% target sustainably in the medium term in line with the MPC’s remit. The Committee has judged since last autumn that monetary policy needs to be restrictive for an extended period of time until the risk of inflation becoming embedded above the 2% target dissipates.
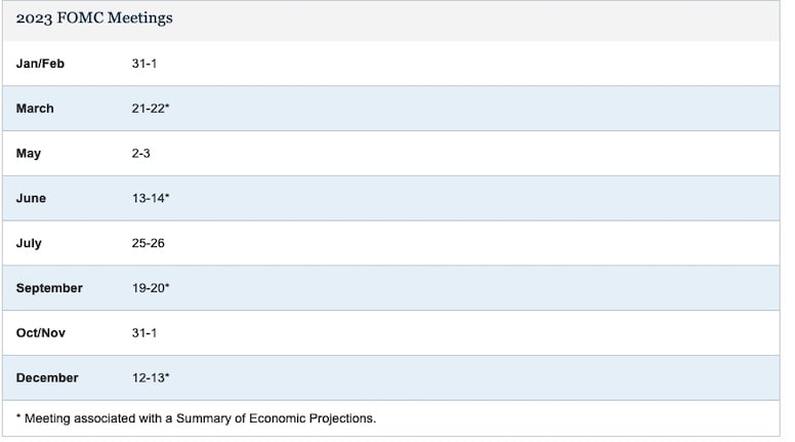
The US central bank - the Federal Reserve opted to maintain its target range for the federal fund rate at 5.25% to 5.50%. Federal Reserve officials left interest rates unchanged at their June meeting on Wednesday and predicted that they will cut borrowing costs just once before the end of 2024, taking a cautious approach as they try to avoid declaring a premature victory over inflation.
The European Central Bank (ECB) made a big move in June, cutting interest rates for the first time since 2019. This decision, announced by ECB President Christine Lagarde, marks a pivotal moment in the ECB's monetary policy, reflecting a shift in response to evolving economic conditions in the Eurozone.
The ECB reduced its key interest rates by 25 basis points, bringing the main refinancing operations rate to 4.25%, the marginal lending facility rate to 4.50%, and the deposit facility rate to 3.75%. This decision was driven by several factors, primarily the need to support economic recovery and address inflation dynamics.
In latest central bank moves, the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) voted 7 to 2 in favour of maintaining the base rate at 5.25% for the seventh consecutive month. Monetary policy will need to remain restrictive for sufficiently long to return inflation to the 2% target sustainably in the medium term in line with the MPC’s remit. The Committee has judged since last autumn that monetary policy needs to be restrictive for an extended period of time until the risk of inflation becoming embedded above the 2% target dissipates.
The US central bank - the Federal Reserve opted to maintain its target range for the federal fund rate at 5.25% to 5.50%. Federal Reserve officials left interest rates unchanged at their June meeting on Wednesday and predicted that they will cut borrowing costs just once before the end of 2024, taking a cautious approach as they try to avoid declaring a premature victory over inflation.
The European Central Bank (ECB) made a big move in June, cutting interest rates for the first time since 2019. This decision, announced by ECB President Christine Lagarde, marks a pivotal moment in the ECB's monetary policy, reflecting a shift in response to evolving economic conditions in the Eurozone.
The ECB reduced its key interest rates by 25 basis points, bringing the main refinancing operations rate to 4.25%, the marginal lending facility rate to 4.50%, and the deposit facility rate to 3.75%. This decision was driven by several factors, primarily the need to support economic recovery and address inflation dynamics.
Fed Funds Rate ...
In the latest move, the June meeting, the Federal Reserve held interest rates unchanged. The target range for the Fed Funds Rate was maintained at 5.25% and 5.5%.
Federal Reserve officials left interest rates unchanged at their June meeting and predicted they will cut borrowing costs just once before the end of 2024, taking a cautious approach as they try to avoid declaring a premature victory over inflation.
Jerome H. Powell, the Fed chair, made clear in a post meeting news conference that officials were taking a careful and conservative approach after months of bumpy inflation data.
Inflation CPI eased down to 3.0 % in June from 3.3% in May. The underlying rate (excluding food and energy costs) was 3.3% (3.4%.)
Growth in the U.S. was 2.9% in the first quarter, compared to growth of 2.5% in 2023.. The US economy is in better shape than economists had expected. A strong labor market, sturdy consumer spending and now easing inflation have fueled hopes that the US will avoid a downturn.
The Fed JUNE outlook, forecasts growth of 2.1% in 2024 and 2.0% in 2025 and 2026. We model growth at 2.5% in 2023, 2024, and 2025.
We continue to model U.S. base rates peaking at 5.25% in 2024 moving to 4.75% in late 2024. The Fed funds rate projection (FOMC June) is 5.1% in 2024, 4.1% in 2025 and 3.1% in 2026.
The Fed Blue Dot forecasts suggest the Long Run average rate in the U.S is now 2.80%. Our model rate is around the 4.00% -4.50% level. Ten Year Bonds trade at just over 4.2% this morning,
In the latest move, the June meeting, the Federal Reserve held interest rates unchanged. The target range for the Fed Funds Rate was maintained at 5.25% and 5.5%.
Federal Reserve officials left interest rates unchanged at their June meeting and predicted they will cut borrowing costs just once before the end of 2024, taking a cautious approach as they try to avoid declaring a premature victory over inflation.
Jerome H. Powell, the Fed chair, made clear in a post meeting news conference that officials were taking a careful and conservative approach after months of bumpy inflation data.
Inflation CPI eased down to 3.0 % in June from 3.3% in May. The underlying rate (excluding food and energy costs) was 3.3% (3.4%.)
Growth in the U.S. was 2.9% in the first quarter, compared to growth of 2.5% in 2023.. The US economy is in better shape than economists had expected. A strong labor market, sturdy consumer spending and now easing inflation have fueled hopes that the US will avoid a downturn.
The Fed JUNE outlook, forecasts growth of 2.1% in 2024 and 2.0% in 2025 and 2026. We model growth at 2.5% in 2023, 2024, and 2025.
We continue to model U.S. base rates peaking at 5.25% in 2024 moving to 4.75% in late 2024. The Fed funds rate projection (FOMC June) is 5.1% in 2024, 4.1% in 2025 and 3.1% in 2026.
The Fed Blue Dot forecasts suggest the Long Run average rate in the U.S is now 2.80%. Our model rate is around the 4.00% -4.50% level. Ten Year Bonds trade at just over 4.2% this morning,
Bank Base Rate ...
At the latest MPC meeting in June, the committee voted by seven votes to two, to hold base rate at 5.25%. Monetary policy will need to remain restrictive for sufficiently long to return inflation to the 2% target sustainably in the medium term in line with the MPC’s remit. The Committee has judged since last autumn that monetary policy needs to be restrictive for an extended period of time until the risk of inflation becoming embedded above the 2% target dissipates.
Inflation, CPI eased to 2.0% in May from 2.3% in April. Core inflation, moved to 3.5% from 3.9%. Food inflation eased to 1.6% from 2.8%. Energy costs held at -27.1%. Service sector inflation eased to 5.7% from 5.9%. Goods inflation dropped to -1.3% from -0.8% .
CPI inflation was expected to fall to target 2.0% in the second quarter, according to forecasts from the OBR and The Bank of England. The Bank expects CPI inflation to average 2.5% in the final quarter. The OBR anticipates inflation to remain below target for the rest of the year, closing at 1.4% in the final quarter.
So what can we make of it all? The Bank remains concerned about the high level of wage settlements and service sector inflation. For the moment, our overall forward guidance outlook remains unchanged. We expect a series of two base rate cuts in the current year possibly beginning in August. We model base rates at 4.5% in the final quarter or possibly Q1 2025, but not much more to follow in 2025.
* Long Term Note : In the UK, prior to the Great Financial Crash [2000 - 2008] the average inflation rate was 2.0%, the average UK bank rate was 4.50%. Ten year gilt yields averaged 4.50%, real GDP growth averaged 2.5%, earnings averaged 3.5%, the unemployment rate averaged 5%.
At the latest MPC meeting in June, the committee voted by seven votes to two, to hold base rate at 5.25%. Monetary policy will need to remain restrictive for sufficiently long to return inflation to the 2% target sustainably in the medium term in line with the MPC’s remit. The Committee has judged since last autumn that monetary policy needs to be restrictive for an extended period of time until the risk of inflation becoming embedded above the 2% target dissipates.
Inflation, CPI eased to 2.0% in May from 2.3% in April. Core inflation, moved to 3.5% from 3.9%. Food inflation eased to 1.6% from 2.8%. Energy costs held at -27.1%. Service sector inflation eased to 5.7% from 5.9%. Goods inflation dropped to -1.3% from -0.8% .
CPI inflation was expected to fall to target 2.0% in the second quarter, according to forecasts from the OBR and The Bank of England. The Bank expects CPI inflation to average 2.5% in the final quarter. The OBR anticipates inflation to remain below target for the rest of the year, closing at 1.4% in the final quarter.
So what can we make of it all? The Bank remains concerned about the high level of wage settlements and service sector inflation. For the moment, our overall forward guidance outlook remains unchanged. We expect a series of two base rate cuts in the current year possibly beginning in August. We model base rates at 4.5% in the final quarter or possibly Q1 2025, but not much more to follow in 2025.
* Long Term Note : In the UK, prior to the Great Financial Crash [2000 - 2008] the average inflation rate was 2.0%, the average UK bank rate was 4.50%. Ten year gilt yields averaged 4.50%, real GDP growth averaged 2.5%, earnings averaged 3.5%, the unemployment rate averaged 5%.
Euro Base Rate ...
The European Central Bank (ECB) made a big move this month, cutting interest rates for the first time since 2019. This decision, announced by ECB President Christine Lagarde, marks a pivotal moment in the ECB's monetary policy, reflecting a shift in response to evolving economic conditions in the eurozone.
The ECB reduced its key interest rates by 25 basis points, bringing the main refinancing operations rate to 4.25%, the marginal lending facility rate to 4.50%, and the deposit facility rate to 3.75%. This decision was driven by several factors, primarily the need to support economic recovery and address inflation dynamics.
The timing of the rate cut is crucial. Lagarde emphasized that the decision was based on a revised assessment of the inflation outlook and the strength of monetary policy transmission. The ECB's projections indicate that while inflation has not yet reached the 2% target, it is on a downward trend expected to continue in the coming months. The average inflation rate is projected to decrease to 2% in 2025 and 1.9% in 2026.
Official figures showed that inflation in the Euro Area eased to 2.5 per cent in June from 2.6 per cent in May. Inflation in the European Union edged up to 2.7% In May from 2.6% in April.
We expected the first cut in June with a further two cuts possible before the end of the year, data dependent of course.
The European Central Bank (ECB) made a big move this month, cutting interest rates for the first time since 2019. This decision, announced by ECB President Christine Lagarde, marks a pivotal moment in the ECB's monetary policy, reflecting a shift in response to evolving economic conditions in the eurozone.
The ECB reduced its key interest rates by 25 basis points, bringing the main refinancing operations rate to 4.25%, the marginal lending facility rate to 4.50%, and the deposit facility rate to 3.75%. This decision was driven by several factors, primarily the need to support economic recovery and address inflation dynamics.
The timing of the rate cut is crucial. Lagarde emphasized that the decision was based on a revised assessment of the inflation outlook and the strength of monetary policy transmission. The ECB's projections indicate that while inflation has not yet reached the 2% target, it is on a downward trend expected to continue in the coming months. The average inflation rate is projected to decrease to 2% in 2025 and 1.9% in 2026.
Official figures showed that inflation in the Euro Area eased to 2.5 per cent in June from 2.6 per cent in May. Inflation in the European Union edged up to 2.7% In May from 2.6% in April.
We expected the first cut in June with a further two cuts possible before the end of the year, data dependent of course.
Scenario Comparisons ...
This is the table of scenario comparisons. We would expect UK rates to lag not lead the US pattern. EU rates would follow the US/UK lead. Inflation may subside sooner than expected. Central banks may worry about the shock to growth. This is a scenario not the plan.
We model the long run rate at 4.0%. The Fed Blue dot projections assume 3.50% as the perceived long run rate. In the UK, prior to the Great Financial Crash [2000 - 2008] the average inflation rate was 2.0%, the average UK bank rate was 4.50%. Ten year bond yields averaged 4.50%.
This is the table of scenario comparisons. We would expect UK rates to lag not lead the US pattern. EU rates would follow the US/UK lead. Inflation may subside sooner than expected. Central banks may worry about the shock to growth. This is a scenario not the plan.
We model the long run rate at 4.0%. The Fed Blue dot projections assume 3.50% as the perceived long run rate. In the UK, prior to the Great Financial Crash [2000 - 2008] the average inflation rate was 2.0%, the average UK bank rate was 4.50%. Ten year bond yields averaged 4.50%.
That's all for this week ... "to understand the markets you have to understand the economics" and we do ...
© 2024 John Ashcroft, Economics, Strategy and Financial Markets, experience worth sharing.
© 2024 John Ashcroft, Economics, Strategy and Financial Markets, experience worth sharing.