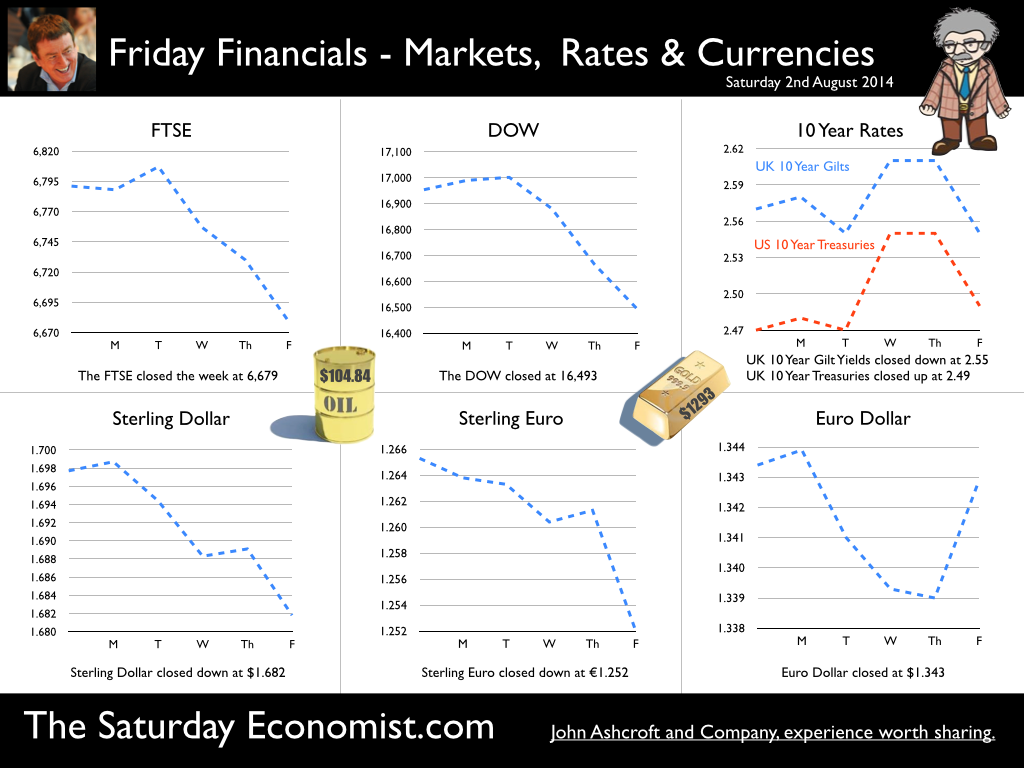
 UK Interest Rates on hold ... No surprise this week as the MPC voted to keep rates on hold and to maintain the asset purchase facility at £375 billion. The decision to increase rates may becoming more finely balanced for some but the news from around the world, will disturb the hawks and give succour to the doves. The rate rise may well be held over into the new year, despite the continued strong performance of the domestic economy. The minutes of the MPC meeting, due later this month, may provide some insight into the overall views of the individual committee members. ECB and Rates ... problems in the East In Europe, rates were kept on hold as Draghi continues to consider QE. Action is needed but the futile process of debt monetisation will do little to offset the economies beset by weak levels of domestic demand. Complaints against the need for labour reform and excessive regulation will largely miss the point. Italy is slipping back into recession with forecasts for the current year downgraded once again to growth of just 0.2%. France will struggle to hit the 1% growth target this year and German export performance is slowing as economies are transfixed by the crisis in Ukraine. Trade sanctions and threat of war are damaging exports from Euro land to Eastern Europe and to Russia. The Euro trading block is now imperilled by it’s very “raison d’être” at inception. Growth in the Euro economies is expected to be just 1% this year with no prospect of a rate rise on the horizon until late 2015 / 2016 at the earliest. Production and Manufacturing ... In the UK, manufacturing data was surprisingly weak in the latest data for June but Euroland is not to blame. Output increased in the month by just 1.9% after strong growth of 3.6% in the first quarter and 4% in April and May. In the second quarter overall growth was up by 3.2%. The underlying data from the Markit/CIPS Manufacturing PMI® suggests strong growth continued into June and July which suggests the latest ONS data may be something of an aberration. [We are adjusting our forecast for the year to growth in manufacturing of 3.4% based on the latest data. Expectations for UK GDP growth are unchanged at 3% following revisions to our service sector forecast.] The Car Market … The SMMT reported strong car sales in July, with new registrations up by 6% in the month and 10% in the year to date. Output increased by 3.5% over the year. The car market is on track to sell 2.45 million units this year. That’s actually higher than the levels achieved in 2007. Assuming output hits the 1.55 million mark, the deficit (trade in cars) will increase to almost 900,000 units. Car manufacturing is benefitting from the recovery in consumer confidence and household spending but the trade deficit will increase as a result of the strength of domestic demand and limitations to domestic capacity. The UK cannot enjoy a period as the strongest growth economy in the Western world without a significant deterioration in the trade balance. Deficit trade in goods and services … And so it continued to prove with the latest trade data. The deficit trade in goods increased slightly in the month of June to £9.5 billion offset by a £7 billion surplus in services. For the second quarter, the deficit was £27.4 billion (trade in goods) and just under £7 billion overall, goods and services. The service sector surplus was £20.5 billion. For the year as a whole, we expect the goods deficit to be £112.3 billion offset by an £80 billion plus serve sector surplus. No threat to the recovery but we still have concerns about the current account deterioration and the drop in overseas investment income. In the first six months of the year, exports of goods have fallen by almost 8% in value and imports have fallen by 4.6%. World trade growth has been subdued in the first six months of the year yet UK domestic demand increased by 3%. Sterling appreciation against the dollar has lead to a translation impact on the trade balance rather than an elasticity effect. Construction and housing ... The latest adjustment for construction data confirms the recovery continues driven by a huge increase in new housing. Total output increased by 5.3% in June, up by 4.8% in Q2 2014 compared to Q2 last year. The total value of new work in the month increased by 5.8% with the volume of new housing increasing by 18% compared to June last year. House Prices ... The increase in housing supply is doing little to assuage the demand for house moves and house prices. Halifax and Nationwide reported prices up by 10% in July. Our transaction model is simple. Activity is a function of house prices and the real cost of borrowing. With mortgages fixed at 4%, the double digit capital appreciation is irresistible to the basic mechanics of a free market. The real cost of borrowing is negative 6%. Demand for housing will continue to out strip supply, despite the regulatory adjustments to the mortgage market. So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed down against the dollar at $1.6774 from $1.682 and unchanged against the Euro at 1.252. The Euro was largely unchanged against the dollar at 1.341. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up slightly at $105.02 from 104.84. The average price in August last year was $111.28. Markets, closed mixed. The Dow closed up 61 points at 16,554 from 16,493 and the FTSE closed down 112 points at 6,567 from 6,679. UK Ten year gilt yields were down at 2.46 from 2.557and US Treasury yields closed at 2.42 from 2.49. Gold was up at $1,305 from $1,293. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.
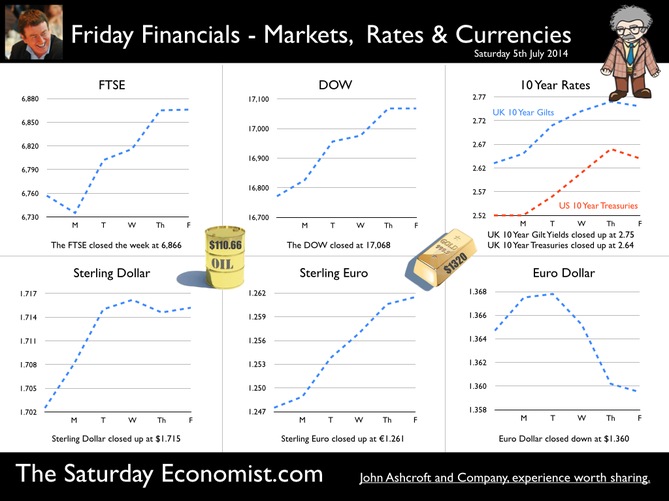
0 Comments
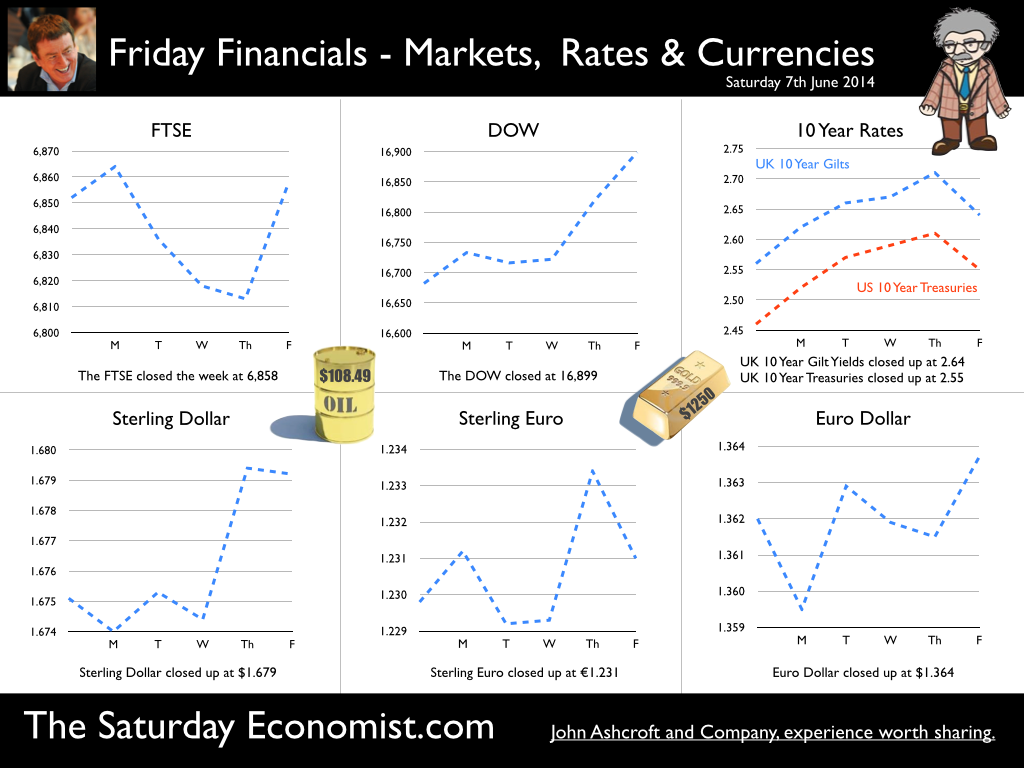
 A letter from America … This week the Professor is in America, reviewing the prospects for the US economy. Despite the pressure on the Bank of England to increase rates before the end of the year, the MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and be the first to leave Planet ZIRP. So what are the prospects of a US rate rise any time soon? Two Fed policy hawks, Richard Fisher of the Dallas Fed and Charles Plosser of the Philadelphia Fed, made comments this week, suggesting they have seen enough evidence to support an interest rate rise earlier than expected. Currently, tapering is expected to continue, extinguishing the asset purchase programme in October. US rates are not expected to rise until Q1 or even Q2 next year. The Prof thinks the latest crop of economics data will take the pressure off the doves to move earlier. Growth in the USA … In the USA, real gross domestic product increased at an annual rate of 4.0 percent in the second quarter of 2014, according to the "advance" estimate released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. 4% sounds quite exhilarating but …. According to our year on year comparison, US GDP Q2 increased by 2.4% in the second quarter compared to Q2 2013. This followed growth of 1.9% in the first quarter - both below trend rate. Our forecast of growth at 2.4% in 2014 is unchanged based on the latest data. The latest GDP estimates ensure there is no pressure on the Fed to accelerate the change in monetary policy. We expect tapering to continue into the Autumn, with a rate rise postponed into 2015. Jobs in the USA … Friday's employment and income reports pointed to steady U.S. job growth with the number of non farm payroll jobs increasing by 209,000. The unemployment rate ticked higher to 6.2% but this a refection of a widening labour pool rather than a slow down in the economy. Moderate expansion in payroll numbers, slightly below expectations, will ensure there is no short term pressure to increase rates anytime soon. Inflation in the USA … The US Consumer Price Index increased by 2.1 percent in the twelve months to June. The PCE (personal consumption expenditure) price index, the Fed's favoured measure of inflation, was up 1.6%. Average hourly earnings of private-sector workers were up 2.0% from a year earlier, unchanged from the range of the past few years. Growth, jobs, earnings and inflation are all demonstrating trends that are likely to keep the Federal Reserve on course to conclude the bond-purchase program in October but remain cautious about raising short-term interest rates before the end of the year. We would expect US rates to rise in the Spring of 2015. Despite any further increase in The Saturday Economist™ Overheating Index™, the MPC will be reluctant to increase rates this year and open the “Spread with the Fed”. So what of the UK? The latest manufacturing data from Markit/CIPS UK PMI® confirmed the strong output growth continued into July. Production and new orders both continued to rise at robust, above long-run average rates in the month. At 55.4, down from 57.2 in June, the headline index posted the lowest reading in one year but remained well above the survey average of 51.5. No need to worry about manufacturing output! Something to worry about … Ben Broadbent, Deputy Governor for monetary policy, Bank of England, made a speech in London this week. His theme - “The UK Current Account Deficit”. Last year the UK current account deficit was 4.5% of GDP. That’s the second-highest annual figure since the Second World War. So is the near record deficit a threat to growth? The Deputy Governor concludes the “significance [of the deficit] depends on the health of a country’s net foreign asset position and more fundamentally, on the trust in its institutions”. “…having a balanced net asset position seems to reduce the threat from a large current account deficit, as does a floating currency.” Now that is concerning. In the 80’s Chancellor Lawson argued the Balance of Payments “doesn’t matter”. It does and in the end it did! Interest rates had to rise dramatically to curtail domestic demand. In the current cycle, the deficit, trade in goods, is offset in part by the service sector surplus. At around 2% to 2.5% of GDP, the deficit is not a threat to growth. The collapse in overseas earnings on the other hand is a more serious concern. A current account deficit of 4.5% is unsustainable. A dismissive speech at Chatham House will not disguise the extent of the problem, rule or no rule. So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed down against the dollar at $1.682 from $1.698 and down against the Euro to 1.252 from (1.2653). The Euro was unchanged against the dollar at 1.343. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $104.84 from 108.30. The average price in August last year was $111.28. Markets, closed down. The Dow closed down 460 points at 16,493 from 16,953 and the FTSE was down 12 points at 6,679 from 6,791. UK Ten year gilt yields were down at 2.55 from 2.57 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.49 from 2.47. Gold was unchanged at $1,293 from $1,294. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. 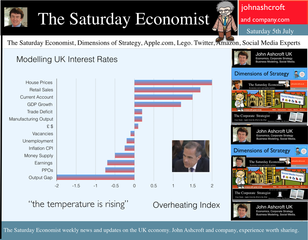 I made a trip to Liverpool this week. It was the Battle of the Economists, part of the International Festival of Business programme. Eight top economists were “in the ring” swapping punches. I “refereed” the morning event and hosted the Question Time session. It was a great event in the IFB calendar with lots of interesting perspectives on the world and UK economy. No blood spilled, nor egos bruised the outcome! To close the session, I asked the panel for views on when UK interest rates would begin to rise. Some argued for an immediate rate rise, most expected rates to rise in February next year and a few expected rates to rise in the November this year. As we said last week, “It is true there have been a lot of conflicting signals about when rates will rise! Following Mark Carney’s Mansion House speech, the odds in favour of a rate rise before the end of the year increased but then lengthened slightly, on the low inflation figures for May and the strength of sterling ”. “Don’t watch my lips - watch the data!” the new forward guidance from the Governor. This week, the data continued to suggest the rate rise would be sooner rather than later. House prices up almost 12% … House prices increased by almost 12% in the year to June according to Nationwide. In London prices increased by 26%. The price of a typical property in London, reached the £400,000 level with prices 30% above the 2007 highs. Should we be concerned? Of course but the rate of increase in house prices of itself, will not lead to an increase in interest rates necessarily. Sir Jon Cunliffe, Deputy Governor for Financial Stability at the Bank of England was in Liverpool this week. “The main risk we see arising from the housing market is the risk that house prices continue to grow strongly and faster than earnings. The concern is the increase in prices leads to higher and more concentrated household indebtedness.” The Bank is not worried about the rise in house prices per se. The FPC (Financial Policy Committee) is concerned about the risk to the banking sector from high household indebtedness exposed to the inevitable rate rise and potential collapse in asset prices. The introduction of measures on interest rate multiples and leverage, the confines of policy intervention for the moment. Car Sales up 10.6% year to date … The strength of the housing market demonstrates the strength of consumer confidence and spending. The economy is growing at 3% this year, retail sales were up by almost 4.5% in the first five months of the year, car sales were up by 6% in June and by 11% in the first six months. We are forecasting registrations will be over 2.4 million in 2014, higher than the pre recession levels recorded in 2007, placing additional pressure on the balance of payments in the process. Yet rates remain pegged at 0.5%! Does this continue to make sense? PMI Markit Purchasing Managers’ Index® Survey Data The influential PMI Markit surveys continue to demonstrate strong growth in the economy into June. In manufacturing, strong growth of output, new orders and jobs completed a robust second quarter. In construction, output growth continued at a four-month high and job creation continued at a record pace. In the service sector, the Business Activity Index, recorded 57.7 in June. The survey produced a record increase in employment with reports of higher wages pushing up operating costs. The Manchester Index™- nowcasting the UK economy The Manchester Index™, developed from the GM Chamber of Commerce Quarterly Economic Survey, slowed slightly from 35.1 in the first quarter to 33.6 in the second quarter, still well above pre recession levels. The data within the survey, confirms our projections for growth in the UK economy this year of 3%, moderating slightly to 2.8% in 2015. So when will rates rise ? The Saturday Economist Overheating Index revealed ... At the GM Chamber of Commerce Quarterly Economics Survey yesterday, we revealed the “overheating Index”. This is a summary of fourteen key indicators which form the basis of any decision to increase rates by the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC). The strength of consumer spending, reflected in house prices, retail sales and car sales would argue in favour of a rate rise earlier rather than later, as would the growth in the UK economy at 3% above trend rate. On the other hand, inflation, reflected in retail prices and manufacturing prices remain subdued. Despite the strength of the jobs market, earnings remain below trend levels. The decision, on when to increase rates, remains finely balanced for MPC members at this time. Our overheating index is broadly neutral but tipped slightly in favour of a rate rise now. By the final quarter of the year, assuming earnings and inflation rally from current levels, the decision will be much more clear cut. Based on data from the Overheating Index, we expect rates to rise before the end of the year. Clearly markets think so too ... So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed up again against the dollar at $1.715 from $1.702 and up against the Euro to 1.261 from (1.247). The Euro moved down against the dollar at 1.360 from 1.365. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $110.66 from $111.35. The average price in June last year was $102.92. Markets, US closed up on the strong jobs data. The Dow closed above the 17,000 level at 17,068 from 16,771 and the FTSE was also up at 6,866 from 6,757, the move above 7,000, too much for the moment. UK Ten year gilt yields were up at 2.75 from 2.63 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.64 from 2.63. Gold was up slightly at $1,320 from $1,316. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. The Manchester Index™ The influential Manchester Index™, is developed from the GM Chamber of Commerce Quarterly Economic Survey. It is a big survey which is comprehensive, authoritative and timely. Now we also have the Manchester Index™. The Manchester Index™ is an early indicator of trends in both the Manchester and the UK economy. Using the Manchester Index we are in a great position to “nowcast” the UK economy and get a pretty good steer on employment and investment in the process.  Earlier this month is his speech at the Mansion House, Mark Carney, Governor of the Bank of England, referenced the Sterling Crisis of 1931 and imbalances within the economy. “We need balance. One has only to look back to 1931 when Britain’s economic prospects were strained by a large budget deficit and a deteriorating balance of payments. In 1931 the UK faced a balance of payments crisis and a run on the pound sterling which in the end led to a negation of the Gold peg and the dollar pricing of $4.86. By modern standards the deficit was no big deal. In 1929, the country had a credit balance (current account) of some £100 million falling to £30 million in 1930. In 1931 there was an estimated debit balance of £90 to £120 millions. It was this anticipated deficit on current account that led to a run on Sterling and a repatriation of assets particularly to France and the USA. The problem for the balance of payments was a deterioration in the net receipts from invisible exports largely as a result of the fall in international trade and collapse of shipping revenues. The government was unwilling to raise interest rates to defend the currency given the overwhelming concern re unemployment. The visible account had long been in substantial deficit, despite a surplus on manufactures and semi manufactures. Imports of raw materials and food, particularly food, meant that exports of manufactures and a surplus in invisible earnings had to finance the food bill of the UK population. In 1931, food exports totalled £39 billion but the import bill was £377 billion producing a deficit of £338 million. The proposition to remedy the balance of payments problem was to eat less, import fewer manufactures and export more. Food, drink and tobacco imports should be reduced by 7%, manufactured goods imports should be reduced by 25% and exports of manufactures increased by 25%. A combination of import tariffs and duties would assist in the process. Certain items were considered to be non-essential including shell fish, game, pickles and pickled vegetables, precious stones, feathers, flowers, plants and bulbs. The category of non essentials, totalled £13 million. The “pickled imports” alone cost the UK £6,000 such was the level of detail in the analysis. In 1930 and 1931, the deficit on merchandise trade was £386m in both years and this was offset by invisible receipts of £400m – £420m in 1931, falling to £285m to £315m in 1931 largely as a result of the fall in income from overseas investments. In 1930, the visible deficit was equal to almost 9% of GDP but thanks to the surplus on invisible account the current account was in balance. It was argued there is no problem of the balance of trade so long as the “£ is free to move” as, if the balance is adverse, sterling will automatically fall to the point necessary to maintain equilibrium. “The real problem is to secure such a balance of payments as is consistent with a reasonable exchange values of the £.” (Committee on the Balance of Trade – report January 19th 1932). In September 1931 the British Government suspended obligations due under the Gold Standard Act of 1925 which required the bank to sell gold at a fixed price. As the statement from the Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald explained. “In the last few days the international financial markets have been “demoralised” and seem intent on liquidating their foreign assets in a sense of panic. Since the middle of July, funds amounting to more than £200 million have been withdrawn from the London market. The withdrawals have been met partly from gold and foreign currency held by the Bank of England, and short term credits of £130 million from the USA and France.” By September 1931, reserves were exhausted. In a chilling note from the Bank of England to the Prime Minister, the Deputy Governor E M Harvey reported : Gentlemen, I am directed to state that the credits for $125,000,000 (£25.7m) and FFs. 3,100,000,000, (£25m) arranged by the Bank of England in New York and Paris respectively, are exhausted, and that the credit for $200,000,000 arranged in New York by His Majesty's Government, together with credits for a total of FFs. 5 millions negotiated in Paris, are practically exhausted also. The heavy demands for exchange on New York and Paris still continue. Under these circumstances, the Bank consider that, having regard to the above commitments and to contingencies that may arise, it would be impossible for them to meet the demands for gold with which they would be faced on withdrawal of support from the New York and Paris exchanges. The Bank therefore feel it their duty to represent that, in their opinion, it is expedient in the national interest that they should be relieved of their obligation to sell gold under the provisions of Section 1 subjection 2 of the Gold Standard Act, 1925. I am, Gentlemen, Your obedient Servant. And so it was, the UK abandoned the Gold Standard, the Pound was left to float, to a level which will automatically produce equilibrium. The rest “as they say” is history. This article was originally posted in April 2011  Deficits with inky blots and rotten parchment bonds sustained - of Balance of Payments and Public Sector Finances. Earlier this month is his speech at the Mansion House, Mark Carney, Governor of the Bank of England, referenced the Sterling Crisis of 1931 and imbalances within the economy. “We need balance. One has only to look back to 1931 when Britain’s economic prospects were strained by a large budget deficit and a deteriorating balance of payments. In the ensuing crisis, the government of the day resigned, sterling was forced off the gold standard" [and the Governor of the day went back to Canada.] In 2014, despite significant internal and external deficits, neither the resignation of the government, nor the repatriation of the Governor of the Bank of England appears imminent. It is however, worth revisiting 1931 and recalling the worlds of Sir Warren Fisher, permanent secretary to the Treasury. In September of that year, Sir Warren Fisher, warned Cabinet, of the Balance of Payments Crisis and the National Budget problem - "Deficits with inky blots and rotten parchment bonds sustained". He could easily have been talking of the present day, QE and debt monetisation. Trade Deficit ... Fisher 1931: The seriousness of the financial difficulties which are engaging public attention is perhaps not fully realised. The root cause of the "run on Sterling" on the part of the foreign depositor is the fact of our living beyond our means as evidenced by our ordering from abroad more goods than we could pay for and therefore our owing to other countries more in dollars and francs than they owe to us in sterling.” Public Sector Finances … Fisher 1931: Closely associated with this fact in the foreign mind is the question of our national Budget. After the war a certain number of countries continued to have difficulties in balancing their budgets and instead of pulling in their belts, resorted to the expedient of meeting deficits by printing innumerable bank or currency notes. Whenever this was done, the national currency lost much or all of its value i.e. purchasing power, and with the corresponding rise in prices, hardship, even hunger, was widespread. Consequently, when any of these countries subsequently desired financial assistance from other countries before the citizens of the latter could be induced to lend, they insisted on the borrowing country balancing its budget. And no one was more emphatic than ourselves in preaching this doctrine. National Budget … Fisher 1931: A national Budget has thus come to be regarded as a touchstone of a country's financial stability second only in importance to its international balance of trade; and if, as the case at present with us, we are "down" on our balance of trade with other countries, foreigners to whom we owe money automatically turn a microscope on to our Budget. And if the Budget is not really balanced, but is merely dressed up to look as though it were, the distrust abroad of our soundness would be intensified. Any expectation that we might continue on a "rake's progress" would complete the destruction of international confidence and thus result in the final collapse of our greatest asset, i.e. our credit. Living beyond our means … Fisher 1931: The remedy is to reverse the process which has been responsible for the trouble, and this means that instead of living at a level which has entailed ordering abroad more goods than we can pay for, we must relate our orders to our capacity to pay. And unless we can produce and sell abroad more goods (including "services") than we have been doing, we shall be forced to cut down our orders abroad, and our and our standard of living must be reduced accordingly. Consequences ... If not the epitaph of us English of to-day will be written by historians to come in Shakespeare' words (Richard II , Act 2, Scene l ) "England, bound in with the triumphant sea, Whose rocky shore beats back the envious siege of watery Neptune, Is now bound in with shame, with inky blots and rotten parchment bonds. That England, that was won’t to conquer others, hath made a shameful conquest of itself". Lessons from History And so history is revisited. With inky blots and rotten bonds sustained. The latest data on the Public Sector Finances is hardly reassuring and the trade deficit will continue to present a problem for an economy growing faster than major trading partners. Note "By the Secretary, The attached memorandum by Sir Warren Fisher is circulated to the Cabinet by instructions from the Prime Minister. (Signed) M. P. A. HANKEY Secretary, Cabinet, Whitehall Gardens, SW1. September 14th, 1931. Footnote : Up to this time the pound sterling, has for international purposes been valued and accepted as the equivalent of a gold pound or of 4.00 dollars or 124 Francs. The Financial and Economic Position of the United Kingdom 1931. Memo to Cabinet from Sir Warren Fisher, Permanent Secretary to the Treasury September 1931. Deficits with Inky Blots and Rotten Parchment Bonds sustained. This article was originally published John Ashcroft.co.uk in July 2009. References : Fun with the National Archives : Cabinet Papers  The MPC left rates on hold this week. We will have to wait a few weeks to find out if the vote was unanimous. For the moment the consensus view is likely to have held. But for how long will this be the case? Forward Guidance is already becoming confused by statements from Martin Weale and Charlie Bean. By the Autumn, the Bank may adopt Dr Doolittle’s pushmi.pullyu animal as a mascot. So thin - the margin of spare capacity - for consensus. The timing of rates is likely to become more polarised amongst MPC members. Who will make the first move? The “Wad is on Weale” to be the first to break ranks. UK data suggest rates may rise sooner … The UK data continues to suggest rates may have to rise sooner than forward guidance implies. Car sales in of May were up by almost 8% in the month and by 12% in the year to date. According to Nationwide, house prices increased by 11% in the twelve months to May. The Halifax House Price data suggested house prices increased by almost 9% over the same period. According to Stephen Noakes, Halifax Mortgages Director : “Housing demand is very strong and continues to be supported by a strengthening economic recovery. Consumer confidence is being boosted by a rapidly improving labour market and low interest rates”. Christine Lagarde and the IMF squad were in the UK this week. The IMF has warned that house prices pose the greatest threat to the UK recovery. It called on the Bank of England to enact policy measures "early and gradually" to avoid a housing bubble. The Fund's annual health check, suggested the UK economy has "rebounded strongly” confirming growth would "remain strong this year at 2.9%”. The IMF also suggested growth is becoming “more balanced” but … Trade deficit deteriorates … There was no evidence of rebalancing in the trade figures for April. The trade deficit in goods increased to £2.5 billion in the month as the deficit (trade in goods) increased to almost £10 billion. OK, someone forget to include all the oil data in the month, which may have under stated exports by £700 million but this is a minor detail. We expect the deficit (trade in goods) to be between £112 billion and £115 billion offset by a £50 billion service sector surplus this year. No rebalancing on the trade agenda, as we have long explained. Markit/CIPS UK PMI® Survey Data The Markit/CIPS UK PMI® survey data was also released this week. “The UK manufacturing upsurge continued”. The Manufacturing PMI index was 57.0 in May, down slightly from 57.3 in April. The survey noted strong growth in output and new orders. There was also a sharp rise in construction output. House building remained the strongest performing area of activity. The headline index was signaling growth for the thirteenth successive month at 60.0, compared to 60.8 prior month. The headline service sector index continued in positive territory at 58.6 compared to 58.7 last month. Service sector employment growth increased at the fastest rate in 17 years. Interest rate outlook … The strong growth in consumer spending, retail sales, car sales and the housing market continues. The outlook for output remains strong in construction, manufacturing and the service sector. We expect investment activity to increase this year. The unemployment rate will continue to fall, placing greater pressure on wage settlements, leading to an increase in earnings into the second half of the year. The trade deficit will continue to deteriorate albeit at a rate which is offset by the strength of the service sector surplus. Sterling will probably hold at current levels for the rest of the year. Inflation, will remain around target, such is the weakness of international energy and commodity prices for the near future. With such a strong outlook for the domestic economy, rates should probably be on the rise by the Autumn of this year. However the MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and the ECB. USA and Europe ... In the USA, Friday’s strong jobs report confirmed the economy is improving following the slight setback in the first quarter. Non farm payroll increased by over 200,000 as the unemployment rate held at 6.3%. For the year as a whole, the Fed may downgrade the growth forecast to around 2.7% from 3% currently. For the moment, forward guidance suggests US rates may begin to rise in the second quarter of 2015 but the outlook may be shortened, if the job trends continue. In Europe, the ECB is heading in another direction. The growth forecast within the Eurozone is just 1% this year but officials are concerned about the prospect of deflation. The latest HICP figure confirmed prices increased by just 0.5% compared to 0.7% prior month. The ECB decided to lower the interest rate on the main refinancing operations of the Eurosystem by 10 basis points to 0.15% and the rate on the marginal lending facility by 35 basis points to 0.40%. The rate on the deposit facility was lowered by 10 basis points to -0.10%. To support bank lending to households and business, excluding loans for house purchase, the ECB will be conducting a series of targeted longer-term refinancing operations (TLTROs) valued at €400 billion over a four year period. The scheme follows the success of the UK Funding for Lending Scheme. So what of forward guidance … Domestic considerations suggest UK rates should be on the rise towards the end of the year. For the moment, forward guidance in the UK and the USA suggests rates will be held until the second quarter of 2015. This may change, if the trends in job growth continue here and in the USA. In Europe, forward guidance is more concerned with the prospects of deflation and a “lost decade”. An increase in rates is not on the “horizon” nor even in the appendix. So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed up against the dollar at $1.679 from $1.675 and unchanged against the Euro at 1.231 (1.230). The dollar closed broadly unchanged at 1.364 from 1.362 against the euro and at 102.53 (101.80) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $108.48 from $109.35. The average price in June last year was $102.92. It is summer after all. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,899 from 16,682 and the FTSE moved up to 6,858 from 6,852. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.64 (2.56) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.55 from 2.46. Gold held at $1,250 from $1,251. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. |
The Saturday EconomistAuthorJohn Ashcroft publishes the Saturday Economist. Join the mailing list for updates on the UK and World Economy. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
| The Saturday Economist |
The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The presentation should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.
|
The Saturday Economist, weekly updates on the UK economy.
Sign Up Now! Stay Up To Date! | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed