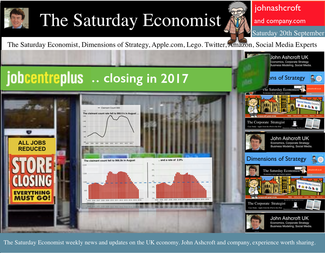
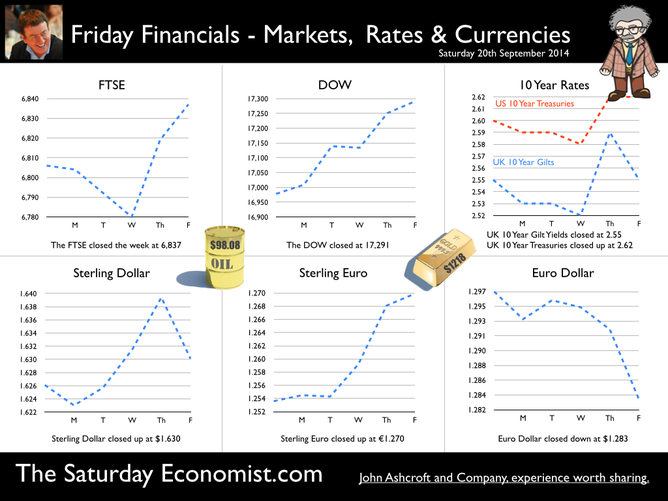
 The prospect of a UK base rate rise before the end of the year receded this week with the release of latest data on inflation and earnings … Retail Prices … Retail price inflation CPI basis slowed to 1.5% in August from 1.6% prior month. Falls in the prices of motor fuels and food provided the largest downward contributions to the change in the rate. Markets expect CPI inflation to average 1.7% over the final quarter of the year, significantly below the MPC benchmark 2% target. Don’t worry about deflation too much, service sector inflation actually increased to a rate 2.7%, as goods inflation fell to 0.6%. Manufacturing Prices … Manufacturing output prices actually fell in August, down by -0.3% compared to a fall of -0.1% in July. Input costs, price of materials and fuels bought by UK manufacturers, fell -7.2% in the year to August, compared with a fall of -7.5% in the year to July. Crude oil costs were down by 14% as price of energy and import costs generally benefited from the weakness of world commodity and trade prices. The appreciation of Sterling helped, up by 8% against the dollar in the month. Home food material costs were down by -10%. Evidence that weak food prices at retail level are not really attributable to supermarket food wars after all. For the moment, inflation, or lack of it, is always and everywhere an international phenomenon. World trade prices are weak. Oil price Brent Crude is trading below $100 per barrel compared to $112 last year. Sterling closed at $1.63 this week up by just 3% compared to September last year. A warning perhaps, the currency contribution may be eroding and the dramatic fall in manufacturing costs may soon be reversed. Unemployment data … The number of people unemployed, claimant count basis fell below 1 million in August, the actual figure was 966,500 and a rate of 2.9%. Over the last six months over 200,000 have left the register. At this rate, job centres will be closing by the end of 2017, there will be no one looking for work. Despite the surging jobs market, pay data remains remarkably weak. Average earnings increased by 0.7% in July. Surprising given the rate of jobs growth. Some evidence of compression is more evident in manufacturing pay, up almost 2% and construction, up by 4%. Retail Sales ... Retail sales rallied in August as volumes increased by 3.9% year on year and values increased by 2.7%. Online sales volumes were up by 8.3% accounting for 11% of all retail transactions. Households are spending and will continue to do so. The August ©GfK Consumer Confidence Barometer confirms households are more optimistic, feel better off and believe it is a good time to spend. So what of base rates …? Janet Yellen, head of the Fed, gave additional guidance on the direction of US rates this week. “The Committee currently anticipates that economic conditions may, for some time, warrant keeping the target federal funds rate below levels the Committee views as normal in the longer run”. “A highly accommodative stance remains appropriate”. There was no real change in the police stance. Markets rallied and the Dow closed above 17,000. Analysts do not expect a rate rise in the USA before June next year. So what does this mean for UK rates? Weak growth in Europe, monetary accommodation in the US, low inflation and earnings data in the UK, will push the increase in UK base rates into 2015. Despite the schism on the committee, the MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed. No escape from Planet ZIRP just yet, we may regret the delayed take off in the years ahead. So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling rallied against the dollar to $1.630 from $1.626 and well up against the Euro at 1.270 from 1.254. The Euro was down against the dollar at 1.270 (1.297). Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $98.08 from $97.62. The average price in September last year was $111.60. Markets, move up. The Dow closed at 17,291 from 16,978 and the FTSE closed down at 6,837 from 6,806. UK Ten year gilt yields moved 2.55 from 2.49 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.62 from 2.60. Gold drifted lower at $1,218 from $1,227. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Economics, Strategy and Social Media ... Experience worth sharing. Disclaimer The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. If you do not wish to receive any further Saturday Economist updates, please unsubscribe using the buttons below or drop me an email at [email protected]. If you enjoy the content, why not forward to a colleague or friend. Or they can sign up here
0 Comments
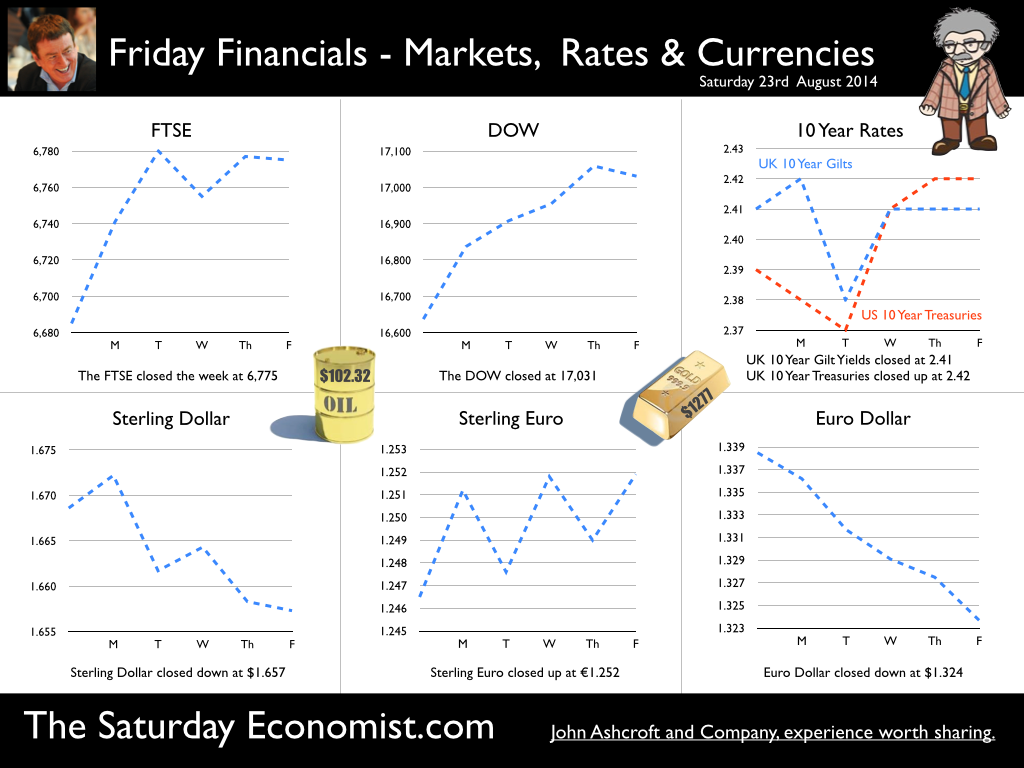
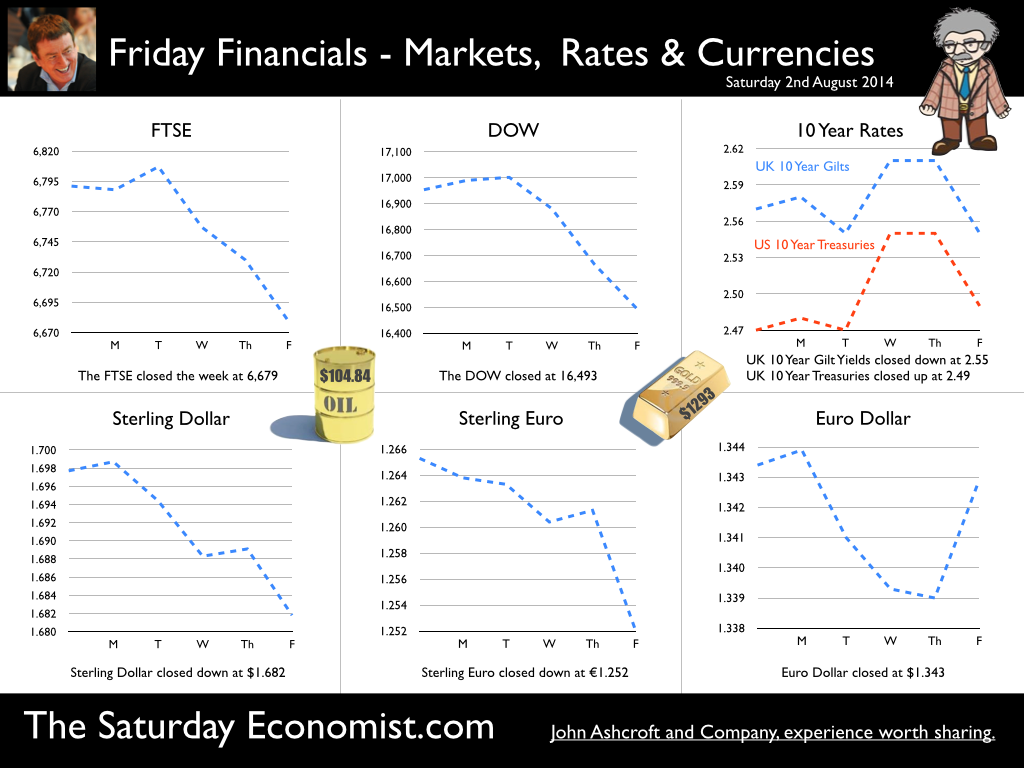
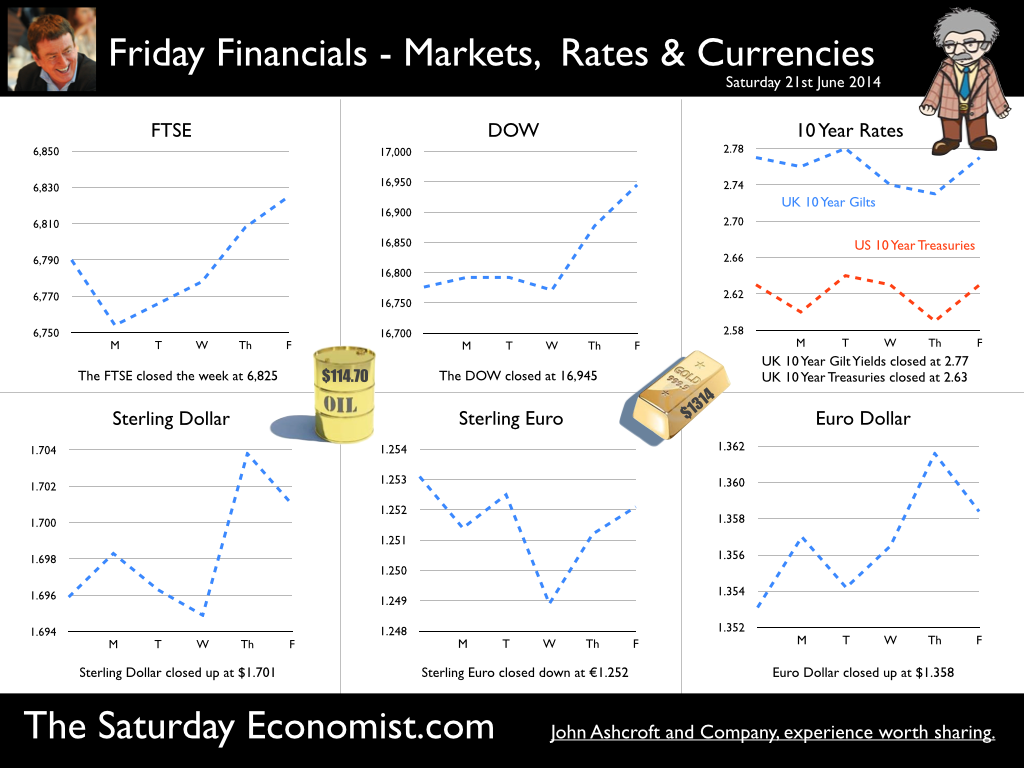
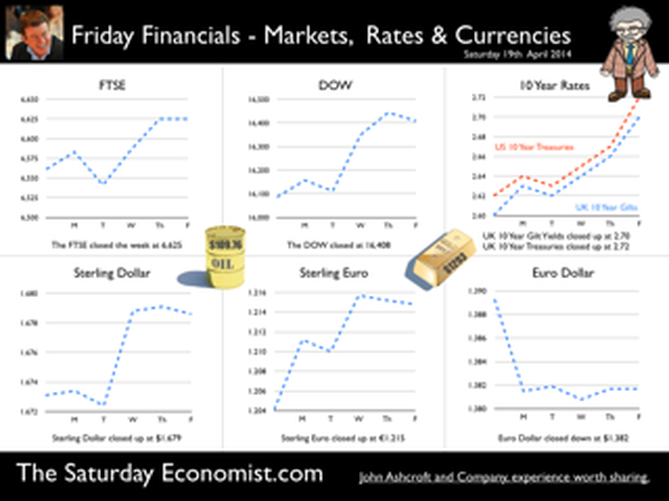
 Jackson Hole, Wyoming. Skiing in Winter and Fly Fishing in Summer, there are several perks to the role of central banker. This week the bankers were in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, fishing for answers to the employment - inflation conundrum. The occasion - the Federal Reserve, Kansas City, Economic Symposium, Jackson Hole, Wyoming. Why Wyoming? You may well ask? In 1982 the conference moved to Jackson Hole (Kansas City district) to persuade Paul Volcker, then chairman of the Fed and an avid fly-fisherman, to attend. Flies and fish were the big lure for the head of the Fed - and so it began. The location, based some 2,000 miles from New York and 5,000 miles from London is not ideal. Communication - in the early days - not always ideal either. Want a copy of the New York Times? The local store stocked today’s and yesterday’s but if you wanted today’s copy, you had to come back tomorrow - delivery lagged a day behind. Monetary Policy and the Muddler Minnow* … This year the theme was Labor Market Dynamics and Monetary Policy. Mario Draghi reassured markets there would be no early rise in rates in Europe! Quelle Surprise! Janet Yellen delivered a lecture on structural, cyclical, secular and frictional unemployment before claiming the mantle of Truman’s two handed economist to explain the Fed’s stance on future monetary policy. On the one hand … “If progress in the labor market continues to be more rapid than anticipated or if inflation moves up more rapidly than anticipated, resulting in faster convergence toward our dual objectives, then increases in the federal funds rate target could come sooner than the Committee currently expects and could be more rapid thereafter.” On the other hand … “If economic performance turns out to be disappointing and progress toward our goals proceeds more slowly than we expect, then the future path of interest rates likely would be more accommodative than we currently anticipate.” Excellent. Yellen then left the room, thrust on a pair of waders, tied on a muddler minnow before making an excellent double spey cast into the River Snake. [*The muddler minnow is currently one of the most favoured trout flies amongst central bankers.] The MPC Minutes … muddying the waters … Back in the UK, the Bank of England released the minutes of the August MPC meeting. Two members of the committee, Martin Weale and Ian McCafferty voted for an increase in base rates by 25 basis points. The Carney consensus has cracked. Charm school is out for the Summer. Markets fell, Sterling rallied, on the prospect of an early rate rise. Inflation Update ... The day before, the ONS released the inflation figures for July. CPI fell to 1.6% from 1.9% prior month. Markets had rallied, Sterling fell, prospects of an imminent rate rise postponed. No one seemed to notice that service sector inflation was unchanged at 2.5%. The overall drop in the headline rate - attributable to goods inflation down to 0.8% from 1.4% in June. So why the drop in goods inflation? Manufacturing output prices were flat but input costs fell by over 7% in the month. Effects of sluggish world trade, weak commodity and energy prices were exacerbated by the translation impact of a stronger Sterling. Government Borrowing … Thursday and the ONS released figures on government borrowing for the month of July. Four months into the year and borrowing remains off track compared to last year and to plan. In the first four months, total borrowing was £37.0 billion compared to £35.2 billion in 2013. In July borrowing was down to £0.7 billion from £1.6 billion last year. An improvement but with an economy expanding by over 3% in the first half of the year, we would expect a big improvement in borrowing given the strength of the recovery. Government spending is not the problem, nor VAT receipts up by 5%. The problem is revenues from income and capital gains tax are actually down on prior year over the first four months of the fiscal year. In part this is a result of strong receipts in the first quarter last year which may level out in due course. Compared to two years ago, revenues are up 5%. Even so, for the year as a whole the Chancellor will still have some work to do if the OBR target is to be met. Retail Sales … Retail sales in July were up by 2.6% after growth of 4% in the first half of the year. A disappointment, perhaps. Internet sales were up by 11% accounting for 11% of all retail activity. It will take more than a few digital mannequins to reverse fortunes on the high street but it is a tad to soon to make the call about a slow down in overall activity. The house market remains strong in terms of prices and the Council of Mortgage Lenders reported a 15% increase in gross mortgage leading last month. So what of base rates … The MPC minutes suggested the rate rise could come earlier than expected but news on inflation and retail sales suggest the rates will be kept on hold until 2015. No rate rise in prospect in Europe but Janet Yellen has “nowcast” a muddler minnow into the thought stream. A rate rise in the USA on the cards for Q2 next year or even earlier? Possibly. In the UK - February or June would appear to be the call. So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed down against the dollar at $1.657 from $1.669 but up against the Euro at 1.252 from 1.246. The Euro was down against the dollar at 1.324 (1.246). Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $102.32 from 102.96. The average price in August last year was $111.28. Markets, rallied on the fishing report from Wyoming. The Dow closed up at 17,031 from 16,637 and the FTSE closed up at 6,775 from 6,685. UK Ten year gilt yields were unchanged at 2.41 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.342 from 2.39. Gold was largely unchanged at $1,302. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Economics, Corporate Strategy and Social Media ... Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  A letter from America … This week the Professor is in America, reviewing the prospects for the US economy. Despite the pressure on the Bank of England to increase rates before the end of the year, the MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and be the first to leave Planet ZIRP. So what are the prospects of a US rate rise any time soon? Two Fed policy hawks, Richard Fisher of the Dallas Fed and Charles Plosser of the Philadelphia Fed, made comments this week, suggesting they have seen enough evidence to support an interest rate rise earlier than expected. Currently, tapering is expected to continue, extinguishing the asset purchase programme in October. US rates are not expected to rise until Q1 or even Q2 next year. The Prof thinks the latest crop of economics data will take the pressure off the doves to move earlier. Growth in the USA … In the USA, real gross domestic product increased at an annual rate of 4.0 percent in the second quarter of 2014, according to the "advance" estimate released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. 4% sounds quite exhilarating but …. According to our year on year comparison, US GDP Q2 increased by 2.4% in the second quarter compared to Q2 2013. This followed growth of 1.9% in the first quarter - both below trend rate. Our forecast of growth at 2.4% in 2014 is unchanged based on the latest data. The latest GDP estimates ensure there is no pressure on the Fed to accelerate the change in monetary policy. We expect tapering to continue into the Autumn, with a rate rise postponed into 2015. Jobs in the USA … Friday's employment and income reports pointed to steady U.S. job growth with the number of non farm payroll jobs increasing by 209,000. The unemployment rate ticked higher to 6.2% but this a refection of a widening labour pool rather than a slow down in the economy. Moderate expansion in payroll numbers, slightly below expectations, will ensure there is no short term pressure to increase rates anytime soon. Inflation in the USA … The US Consumer Price Index increased by 2.1 percent in the twelve months to June. The PCE (personal consumption expenditure) price index, the Fed's favoured measure of inflation, was up 1.6%. Average hourly earnings of private-sector workers were up 2.0% from a year earlier, unchanged from the range of the past few years. Growth, jobs, earnings and inflation are all demonstrating trends that are likely to keep the Federal Reserve on course to conclude the bond-purchase program in October but remain cautious about raising short-term interest rates before the end of the year. We would expect US rates to rise in the Spring of 2015. Despite any further increase in The Saturday Economist™ Overheating Index™, the MPC will be reluctant to increase rates this year and open the “Spread with the Fed”. So what of the UK? The latest manufacturing data from Markit/CIPS UK PMI® confirmed the strong output growth continued into July. Production and new orders both continued to rise at robust, above long-run average rates in the month. At 55.4, down from 57.2 in June, the headline index posted the lowest reading in one year but remained well above the survey average of 51.5. No need to worry about manufacturing output! Something to worry about … Ben Broadbent, Deputy Governor for monetary policy, Bank of England, made a speech in London this week. His theme - “The UK Current Account Deficit”. Last year the UK current account deficit was 4.5% of GDP. That’s the second-highest annual figure since the Second World War. So is the near record deficit a threat to growth? The Deputy Governor concludes the “significance [of the deficit] depends on the health of a country’s net foreign asset position and more fundamentally, on the trust in its institutions”. “…having a balanced net asset position seems to reduce the threat from a large current account deficit, as does a floating currency.” Now that is concerning. In the 80’s Chancellor Lawson argued the Balance of Payments “doesn’t matter”. It does and in the end it did! Interest rates had to rise dramatically to curtail domestic demand. In the current cycle, the deficit, trade in goods, is offset in part by the service sector surplus. At around 2% to 2.5% of GDP, the deficit is not a threat to growth. The collapse in overseas earnings on the other hand is a more serious concern. A current account deficit of 4.5% is unsustainable. A dismissive speech at Chatham House will not disguise the extent of the problem, rule or no rule. So what happened to sterling this week? Sterling closed down against the dollar at $1.682 from $1.698 and down against the Euro to 1.252 from (1.2653). The Euro was unchanged against the dollar at 1.343. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $104.84 from 108.30. The average price in August last year was $111.28. Markets, closed down. The Dow closed down 460 points at 16,493 from 16,953 and the FTSE was down 12 points at 6,679 from 6,791. UK Ten year gilt yields were down at 2.55 from 2.57 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.49 from 2.47. Gold was unchanged at $1,293 from $1,294. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. 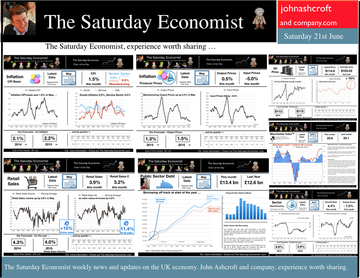 The Manchester Index™ confirms the UK recovery is on track with growth continuing around 3% into the second quarter of the year. The index fell slightly to 33.6 from 35.1, still much higher than pre recession levels. The preliminary results from the GM Chamber of Commerce QES data were available this week. The survey suggests strong growth in manufacturing continues, with slightly more moderate growth in the service sector. The results are in line with our forecasts for the full year - available in the June Economic Outlook. The full results and presentation on the influential Chamber of Commerce QES survey for Q2 will be available on the 4th July. Don’t miss that! Public Sector Finances off track … The strong performance in the economy is slightly at odds with the Public Sector Finances for May, released this week. The UK economy is expanding by just over 3% in the first half of the year. We would expect an improvement in borrowing given the strength of the recovery. Two months into the year and borrowing is off track compared to last year and to plan. In the first two months of the year, total borrowing was up at £24.2 billion compared to £23.2 billion prior year. Strong VAT revenues contributed to a 9% growth in total receipts but expenditure increased by almost 6%, despite a fall in interest payments. Last year’s borrowing figure has been revised to £107.0 billion for the financial year. Good news for the Chancellor but revenues will have to improve and expenditure will have to be contained, if this year’s OBR forecast is to be met. Strong Retail sales in May … Strong retail sales are contributing to the VAT receipts. In May retail sales volumes were up 3.9% compared to last year. This is down on April’s staggering 6.5% growth but we still expect growth of 4.6% in the current quarter and 4.3% for the year as a whole. Internet sales were up by 15%, now accounting for 11.4% of all activity. The online disruption continues. Sales values were up by just 3.2%, contributing to deflation and retail concerns in the High Street. Inflation slows in May … And so it was with the inflation figures. Inflation CPI basis slowed to 1.5% in May, down from 1.8% in April. Service sector inflation was 2.2% and goods inflation held at 0.9%. Falls in transport service costs, notably air fares, provided the largest contribution to the decrease in the rate. Other large downward effects came from food, drinks and clothing. The fall came as something of a surprise, we still expect inflation to track near target (2%) for the year as a whole. Producer Prices no pressure on inflation … No pressure on inflation is evident in the producer price information, released this week. Output prices in May increased by just 0.5% as input costs fell by 5%. Import prices of fuel, oil, food, metals, chemicals, parts, equipment and materials the real story. It is a story of weak international growth in GDP and trade, with slow growth in commodity prices, assisted by the strength of sterling, closing the week above the critical $1.70 level. Monetary Policy and Minutes of the MPC ... So why is Sterling so strong? Statements from Governor Carney that rates may rise “sooner than markets expect" are contrasting with the “Business as Usual” stance from the Federal Reserve. The Fed reduced the forecast GDP 2014 outlook for the US economy to just 2.2% from 3% earlier. Tapering is set to continue but guidelines suggest interest rates will not rise until the second quarter of next year. In the UK, we expect rates to rise in the final quarter of the year. Inflation and earnings suggest that strong growth of itself will not precipitate the rise. The Sterling genie is removing the $1.70 stopper. Who speaks for Sterling? We asked in March last year as the pound headed to the $1.50 level. Sterling look set to test $1.74 in the months ahead unless rate fears are calmed. So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed up against the dollar pushing through resistance at the $1.70 level. Sterling closed up at $1.7010 from $1.696, steady against the Euro at 1.252 (1.253). The Euro strengthened against the dollar at 1.358 from 1.353. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up at $114.70 from $113.07 on Middle East concerns. The average price in June last year was $102.92. The inflation impact cannot be ignored if the a-seasonal pattern persists. Markets, closed up. The Dow closed down at 16,945 from 16,776 and the FTSE was also up at 6,825 from 6,790. UK Ten year gilt yields held at 2.77 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.63 from 2.77 on interest rate trends. Gold moved higher on geo political fears at $1,314 from $1,274. That’s all for this week. Visit the revamped web site. Download our Quarterly Forecast. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. Disclaimer The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. About the Manchester Index™ … The Greater Manchester economy correlates highly with trends in the national economy. The Manchester Index® is an early indicator of trends in both the Manchester and the UK economy. The index is derived from the GM Quarterly Economics Survey which forms part of the British Chambers of Commerce National Survey. Greater Manchester is the largest contributor to this important business survey. We poll 5000 businesses every quarter. As the principal national business survey and the first to be published in each quarter, the results are closely monitored by HM Treasury and the Bank of England Monetary Committee. The GM survey data has a high correlation with the national data. In other key indicators, the unemployment claimant count for example, has a high correlation (over 99%) with the national data set. Our business investment tracker utilises data from capacity and investment intentions to forecast investment in the UK economy. We lag capacity by four quarters and investment intentions by two quarters to model spending.  Janet Yellen was speaking at the Economic Club of New York this week. Three big questions continue to dominate policy formulation at the Federal Reserve. Unemployment, inflation and factors which may push the recovery off track. Actually, that’s more than three but … According to the Fed forecasts, US unemployment is set to fall to around 5.5% by the end of 2016 and inflation will hover just below 2%. “The economy would be approaching maximum employment and price stability for the first time in nearly a decade”. That's NICE! And what of interest rates? “Economic conditions, may for some time warrant keeping short term interest rates below levels the Committee views as likely to prove normal in the longer run”. The markets reacted well. The Dow moved up and the dollar moved down. Sterling moved to $1.679. In March, the Fed chair had given a clear indication that rates would start to rise in the first quarter of 2015. Less than a month later, there was no such clarity. Rates will be on hold until the recovery is well established. As long as it takes. Unemployment rate, the measure of momentum that really matters, to the doves at the Fed. Exogenous Shocks Nowhere in the speech did the “Capsid Bug” feature. According to a report in The Times today, black pod disease and capsid bug infestations are ravaging cocoa crops in West Africa. This shock to supply plus the surging demand from Chinese Chocaholics is causing a cocoa pop. Cocoa beans have jumped in price from $2,680 per tonne in January to over $3,000 per tonne in March. There could be a 115,000 tonne shortfall in supply this year. By next Easter, we may well be eating smaller eggs which cost much more. So much for the threat of world deflation! Does this matter? Well yes. The collapse of the Peruvian anchovy crop in 1972/3 was claimed by many to herald the onset of the hyper inflationary episode of the seventies. OK, the Russian grain famine, the onset of OPEC and the quadrupling of oil prices assisted considerably. But the message is, exogenous shocks from commodity prices can have a greater impact on domestic inflation. Much greater than the Phillips curve paradigm, much beloved by the FOMC, provides. This is clearly demonstrated in the UK economics data released this week. Inflation is falling, employment is rising. World prices mitigated by the appreciation of Sterling are marking the price changes. UK Inflation Inflation CPI basis slowed to 1.6% in March from 1.7% in the prior month. Goods inflation fell to 1.0% and service sector inflation fell to 2.3% (2.4%). Oil related transport costs were dominant in the slow down. Manufacturing output prices increased by just 0.5% as input costs actually fell by 6.5%. The fall in crude oil prices, imported metals, parts and equipment largely explained the fall. Sterling appreciation assisted the process. Sterling averaged $1.66 in March this year compared to $1.51 last year. A 10% appreciation assisting the “deflationary process” significantly. [Oil prices Brent crude basis averaged $108 approximately in both months]. So what of employment? Unemployment figures - Jobcentres will be closing by the end of 2016 Unemployment fell to 6.9% in the three months to February to a level of 2.24 million. This is below the level originally outlined in the Bank of England Forward Guidance in August last year. 7.0% the level at which the Bank would begin to consider an increase in base rates. The claimant count fell by 30,000 to a level of 1.142 million. Over the last three months, the count has fallen by 100,000 and almost 400,000 over the last twelve months. If current rates persist, the labour market will fall to pre recession levels towards the end of the year. By the end of 2016, No one will be left on the list. So this is what they mean by full employment! Jobcentres will have to close! The implications for earnings are evident. Already in February, whole economy earnings increased by 1.9% and wages in manufacturing and construction increased by 3%. We expect a significant acceleration in earnings throughout the year as the labour market tightens considerably. As for base rates, Yellen is signalling the US rates will be kept on hold well into 2015. The Bank of England may well have no such luxury. The MPC will be reluctant to raise rates ahead of the Fed. If this were to happen, despite the inherent structural weakness on trade and the current account, sterling will continue to rise significantly. $1.73 the next target? So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed at $1.679 from $1.673 and at 1.215 from 1.204 against the Euro. The dollar closed at 1.382 from 1.3389 against the euro and at 102.42 against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed at $109.76 from $107.70. The average price in April last year was $101.2. The energy kicker to falling prices may well be over. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,408 from 16,086and the FTSE also closed up at 6,625 from 6,561. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.70 (2.60) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.72 from 2.62. Gold moved lower to $1,293 from $1,318. The pattern is bullish for equities.. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. |
The Saturday EconomistAuthorJohn Ashcroft publishes the Saturday Economist. Join the mailing list for updates on the UK and World Economy. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
| The Saturday Economist |
The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The presentation should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.
|
The Saturday Economist, weekly updates on the UK economy.
Sign Up Now! Stay Up To Date! | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed