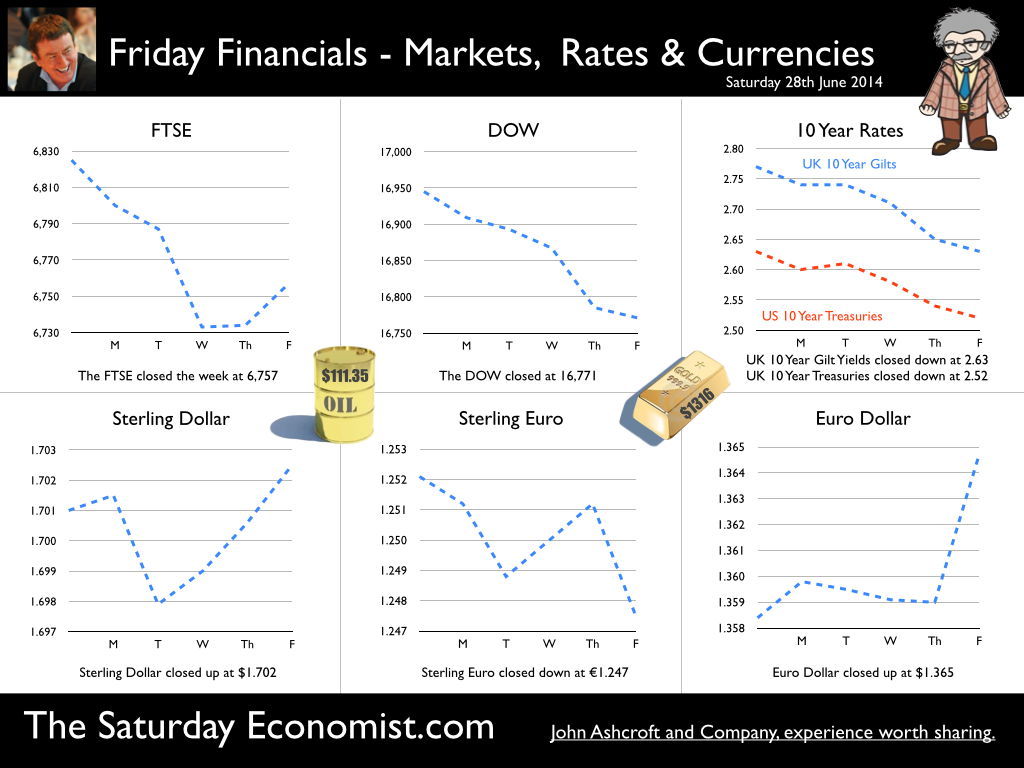
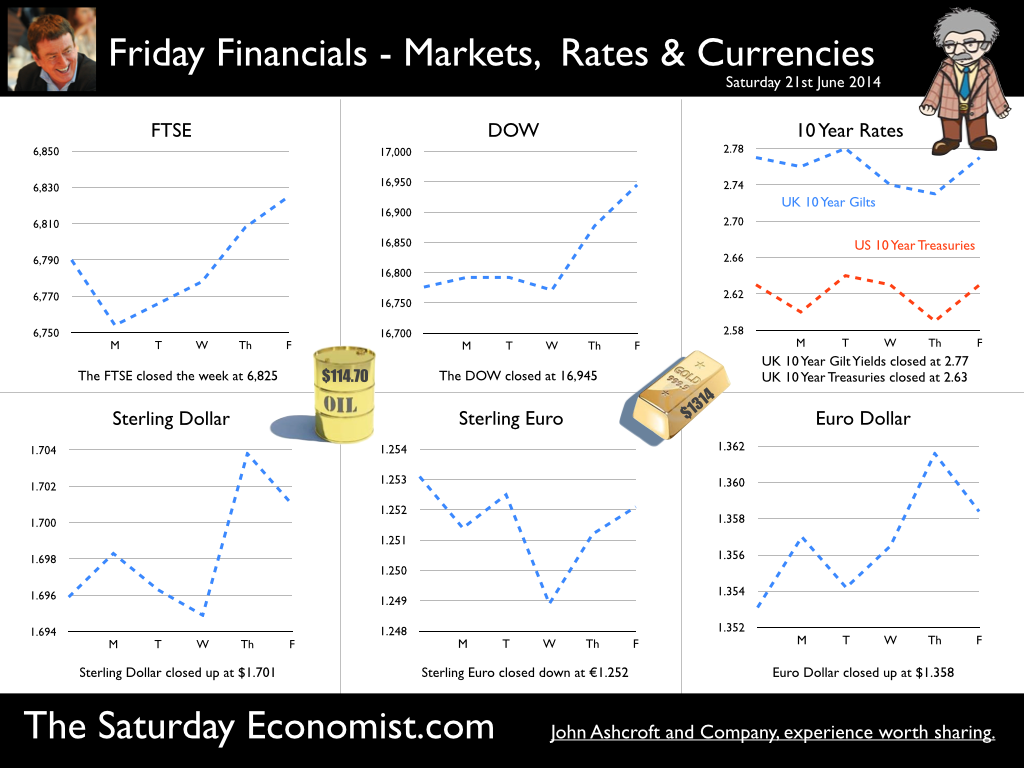
 The Governor was in front of the Treasury Select Committee this week. Pat McFadden raised a laugh about forward Guidance - “The bank is behaving like an unreliable boyfriend, one day hot, one day cold, - people on the other side of the message not really knowing where they stand”. But is that really fair? It is true there have been a lot of conflicting signals about when rates will rise! Following Mark Carney’s Mansion House speech, the odds in favour of a rate rise before the end of the year increased but then lengthened slightly, on the strength of sterling and the low inflation figures for May. The Governor is advising markets, “forward guidance is state contingent”. As the state of the economy changes, the timing of future rate increases will also change. No need to wait for the Quarterly Inflation Report to mark the move. The situation is fluid and dynamic. As the data changes, so will future rate rise probabilities. “Don’t watch my lips - watch the data!” the new guidance. Revisions to GDP data … And so it was, the UK data changed, slightly, this week with the revisions to growth in the first quarter. The ONS revised down growth in Q1 from 3.1% to 3%! This is hardly likely to impact on monetary policy in any way shape or form. The adjustments reflect minor statistical adjustments rather than major structural moves. Our forecast of growth for 3% in 2014 is unaffected by the change. Investment grabbed the headlines, increasing by almost 10% in the quarter. The year on year comparison was against a particularly weak quarter last year. We expect investment growth of over 7% for the year as a whole, using research data derived from the Manchester Index™. [GM Chamber of Commerce research data - capacity and investment intentions]. In the USA, the revisions to GDP growth in the first quarter were much more significant. The headlines confirm growth fell by 2.9% quarter on quarter. Yet, the underlying growth year on year was up by 1.5%. The FOMC expect US growth of 2.2% this year rising to over 3% next. So what of Medium Term Rates … In the UK, the governor would have markets believe rates will rise slowly and thereafter are unlikely to rise above 2.5% in the medium term. In the USA, the Fed present no such illusion. Medium term rates, according to members of the FOMC, are expected to rise to 4% plus and some members expect this to occur by 2016. For now, US Bond traders believe the FOMC is too optimistic about the economy. Interest rates will remain low well into this decade. But if it does happen “over there”, is the UK - US spread manageable? Hardly likely. The medium term path of UK base rates is set to return to the 4.0% plus norm in due course, narrowing the divide. As for the timing - well that is another "guidance" issue altogether! So what happened to sterling ... The pound closed up against the dollar closing above the highly significant $1.70 level. Sterling closed at $1.702 from $1.70, slipping against the Euro to 1.247 (1.252). The Euro moved up against the dollar at 1.365 from 1.358. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $111.35 from $114.70 as Middle East concerns cleared slightly. The average price in June last year was $102.92. Markets, closed down. The Dow closed down at 16,771 from 16,945 and the FTSE was also down at 6,757 from 6,825. UK Ten year gilt yields were down at 2.63 from 2.77 and US Treasury yields closed unchanged at 2.63. Gold was steady at $1,316 from $1,314. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.
0 Comments
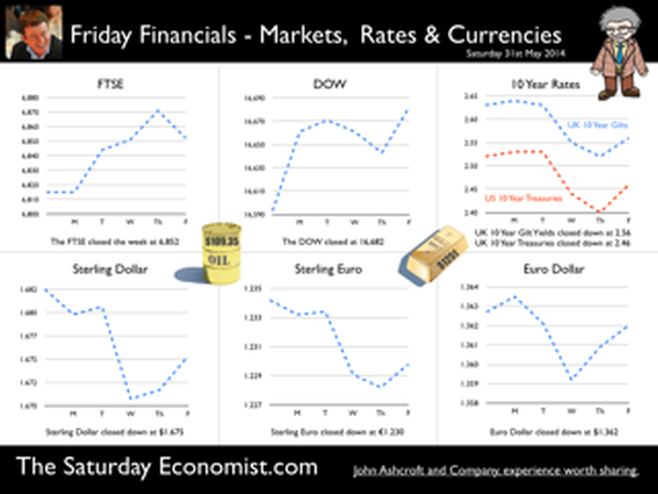
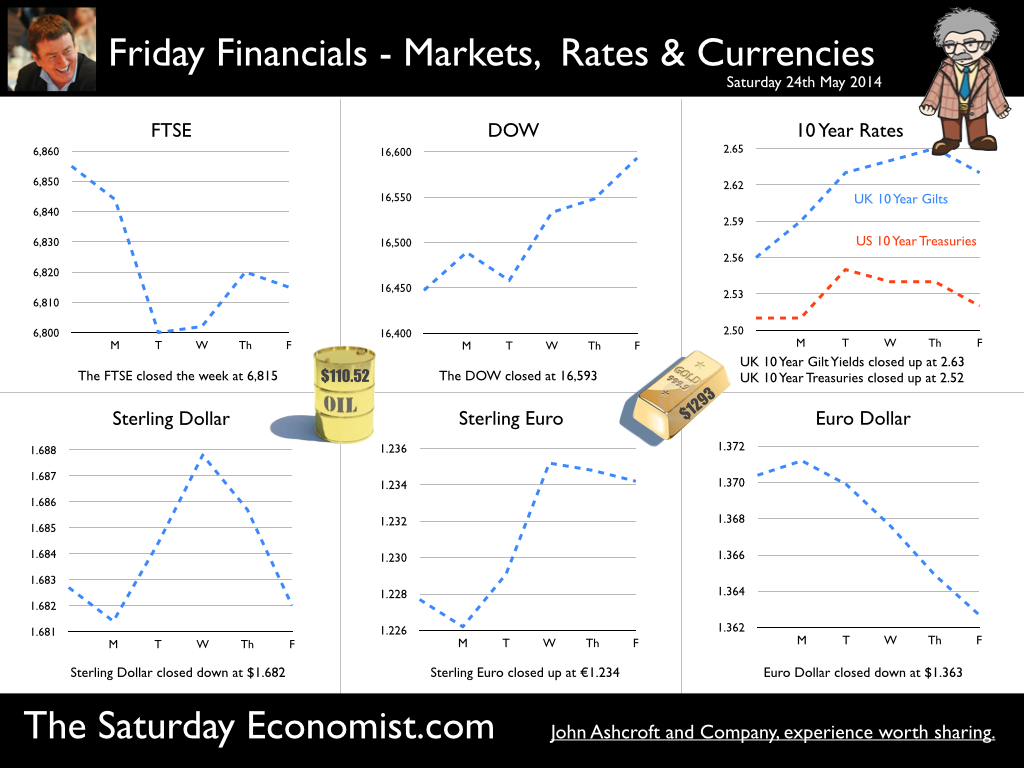
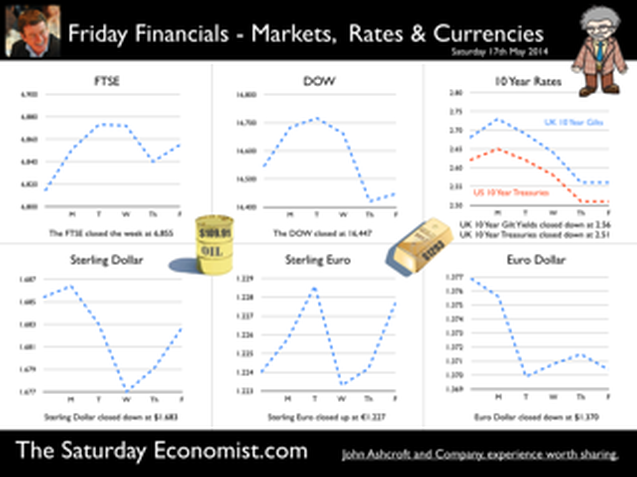
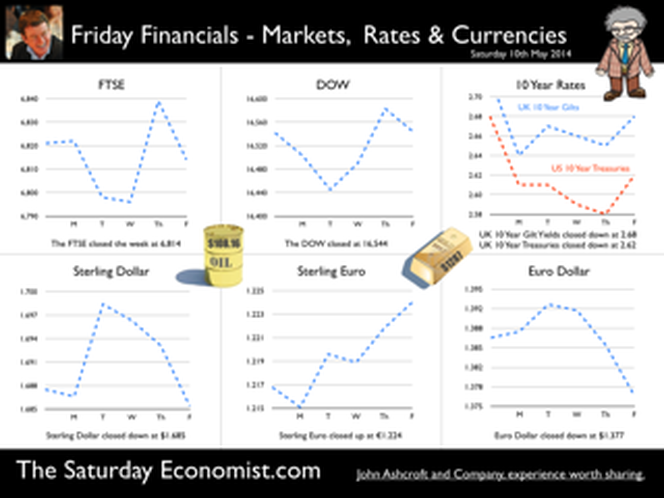
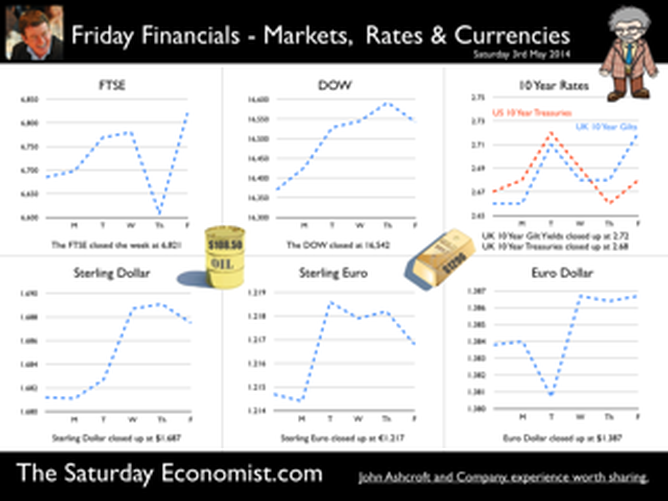
 Earlier this month is his speech at the Mansion House, Mark Carney, Governor of the Bank of England, referenced the Sterling Crisis of 1931 and imbalances within the economy. “We need balance. One has only to look back to 1931 when Britain’s economic prospects were strained by a large budget deficit and a deteriorating balance of payments. In 1931 the UK faced a balance of payments crisis and a run on the pound sterling which in the end led to a negation of the Gold peg and the dollar pricing of $4.86. By modern standards the deficit was no big deal. In 1929, the country had a credit balance (current account) of some £100 million falling to £30 million in 1930. In 1931 there was an estimated debit balance of £90 to £120 millions. It was this anticipated deficit on current account that led to a run on Sterling and a repatriation of assets particularly to France and the USA. The problem for the balance of payments was a deterioration in the net receipts from invisible exports largely as a result of the fall in international trade and collapse of shipping revenues. The government was unwilling to raise interest rates to defend the currency given the overwhelming concern re unemployment. The visible account had long been in substantial deficit, despite a surplus on manufactures and semi manufactures. Imports of raw materials and food, particularly food, meant that exports of manufactures and a surplus in invisible earnings had to finance the food bill of the UK population. In 1931, food exports totalled £39 billion but the import bill was £377 billion producing a deficit of £338 million. The proposition to remedy the balance of payments problem was to eat less, import fewer manufactures and export more. Food, drink and tobacco imports should be reduced by 7%, manufactured goods imports should be reduced by 25% and exports of manufactures increased by 25%. A combination of import tariffs and duties would assist in the process. Certain items were considered to be non-essential including shell fish, game, pickles and pickled vegetables, precious stones, feathers, flowers, plants and bulbs. The category of non essentials, totalled £13 million. The “pickled imports” alone cost the UK £6,000 such was the level of detail in the analysis. In 1930 and 1931, the deficit on merchandise trade was £386m in both years and this was offset by invisible receipts of £400m – £420m in 1931, falling to £285m to £315m in 1931 largely as a result of the fall in income from overseas investments. In 1930, the visible deficit was equal to almost 9% of GDP but thanks to the surplus on invisible account the current account was in balance. It was argued there is no problem of the balance of trade so long as the “£ is free to move” as, if the balance is adverse, sterling will automatically fall to the point necessary to maintain equilibrium. “The real problem is to secure such a balance of payments as is consistent with a reasonable exchange values of the £.” (Committee on the Balance of Trade – report January 19th 1932). In September 1931 the British Government suspended obligations due under the Gold Standard Act of 1925 which required the bank to sell gold at a fixed price. As the statement from the Prime Minister Ramsay MacDonald explained. “In the last few days the international financial markets have been “demoralised” and seem intent on liquidating their foreign assets in a sense of panic. Since the middle of July, funds amounting to more than £200 million have been withdrawn from the London market. The withdrawals have been met partly from gold and foreign currency held by the Bank of England, and short term credits of £130 million from the USA and France.” By September 1931, reserves were exhausted. In a chilling note from the Bank of England to the Prime Minister, the Deputy Governor E M Harvey reported : Gentlemen, I am directed to state that the credits for $125,000,000 (£25.7m) and FFs. 3,100,000,000, (£25m) arranged by the Bank of England in New York and Paris respectively, are exhausted, and that the credit for $200,000,000 arranged in New York by His Majesty's Government, together with credits for a total of FFs. 5 millions negotiated in Paris, are practically exhausted also. The heavy demands for exchange on New York and Paris still continue. Under these circumstances, the Bank consider that, having regard to the above commitments and to contingencies that may arise, it would be impossible for them to meet the demands for gold with which they would be faced on withdrawal of support from the New York and Paris exchanges. The Bank therefore feel it their duty to represent that, in their opinion, it is expedient in the national interest that they should be relieved of their obligation to sell gold under the provisions of Section 1 subjection 2 of the Gold Standard Act, 1925. I am, Gentlemen, Your obedient Servant. And so it was, the UK abandoned the Gold Standard, the Pound was left to float, to a level which will automatically produce equilibrium. The rest “as they say” is history. This article was originally posted in April 2011  Deficits with inky blots and rotten parchment bonds sustained - of Balance of Payments and Public Sector Finances. Earlier this month is his speech at the Mansion House, Mark Carney, Governor of the Bank of England, referenced the Sterling Crisis of 1931 and imbalances within the economy. “We need balance. One has only to look back to 1931 when Britain’s economic prospects were strained by a large budget deficit and a deteriorating balance of payments. In the ensuing crisis, the government of the day resigned, sterling was forced off the gold standard" [and the Governor of the day went back to Canada.] In 2014, despite significant internal and external deficits, neither the resignation of the government, nor the repatriation of the Governor of the Bank of England appears imminent. It is however, worth revisiting 1931 and recalling the worlds of Sir Warren Fisher, permanent secretary to the Treasury. In September of that year, Sir Warren Fisher, warned Cabinet, of the Balance of Payments Crisis and the National Budget problem - "Deficits with inky blots and rotten parchment bonds sustained". He could easily have been talking of the present day, QE and debt monetisation. Trade Deficit ... Fisher 1931: The seriousness of the financial difficulties which are engaging public attention is perhaps not fully realised. The root cause of the "run on Sterling" on the part of the foreign depositor is the fact of our living beyond our means as evidenced by our ordering from abroad more goods than we could pay for and therefore our owing to other countries more in dollars and francs than they owe to us in sterling.” Public Sector Finances … Fisher 1931: Closely associated with this fact in the foreign mind is the question of our national Budget. After the war a certain number of countries continued to have difficulties in balancing their budgets and instead of pulling in their belts, resorted to the expedient of meeting deficits by printing innumerable bank or currency notes. Whenever this was done, the national currency lost much or all of its value i.e. purchasing power, and with the corresponding rise in prices, hardship, even hunger, was widespread. Consequently, when any of these countries subsequently desired financial assistance from other countries before the citizens of the latter could be induced to lend, they insisted on the borrowing country balancing its budget. And no one was more emphatic than ourselves in preaching this doctrine. National Budget … Fisher 1931: A national Budget has thus come to be regarded as a touchstone of a country's financial stability second only in importance to its international balance of trade; and if, as the case at present with us, we are "down" on our balance of trade with other countries, foreigners to whom we owe money automatically turn a microscope on to our Budget. And if the Budget is not really balanced, but is merely dressed up to look as though it were, the distrust abroad of our soundness would be intensified. Any expectation that we might continue on a "rake's progress" would complete the destruction of international confidence and thus result in the final collapse of our greatest asset, i.e. our credit. Living beyond our means … Fisher 1931: The remedy is to reverse the process which has been responsible for the trouble, and this means that instead of living at a level which has entailed ordering abroad more goods than we can pay for, we must relate our orders to our capacity to pay. And unless we can produce and sell abroad more goods (including "services") than we have been doing, we shall be forced to cut down our orders abroad, and our and our standard of living must be reduced accordingly. Consequences ... If not the epitaph of us English of to-day will be written by historians to come in Shakespeare' words (Richard II , Act 2, Scene l ) "England, bound in with the triumphant sea, Whose rocky shore beats back the envious siege of watery Neptune, Is now bound in with shame, with inky blots and rotten parchment bonds. That England, that was won’t to conquer others, hath made a shameful conquest of itself". Lessons from History And so history is revisited. With inky blots and rotten bonds sustained. The latest data on the Public Sector Finances is hardly reassuring and the trade deficit will continue to present a problem for an economy growing faster than major trading partners. Note "By the Secretary, The attached memorandum by Sir Warren Fisher is circulated to the Cabinet by instructions from the Prime Minister. (Signed) M. P. A. HANKEY Secretary, Cabinet, Whitehall Gardens, SW1. September 14th, 1931. Footnote : Up to this time the pound sterling, has for international purposes been valued and accepted as the equivalent of a gold pound or of 4.00 dollars or 124 Francs. The Financial and Economic Position of the United Kingdom 1931. Memo to Cabinet from Sir Warren Fisher, Permanent Secretary to the Treasury September 1931. Deficits with Inky Blots and Rotten Parchment Bonds sustained. This article was originally published John Ashcroft.co.uk in July 2009. References : Fun with the National Archives : Cabinet Papers 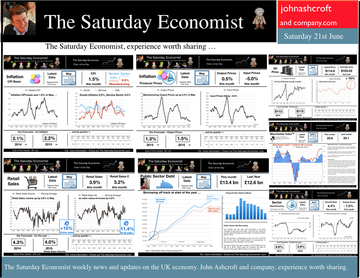 The Manchester Index™ confirms the UK recovery is on track with growth continuing around 3% into the second quarter of the year. The index fell slightly to 33.6 from 35.1, still much higher than pre recession levels. The preliminary results from the GM Chamber of Commerce QES data were available this week. The survey suggests strong growth in manufacturing continues, with slightly more moderate growth in the service sector. The results are in line with our forecasts for the full year - available in the June Economic Outlook. The full results and presentation on the influential Chamber of Commerce QES survey for Q2 will be available on the 4th July. Don’t miss that! Public Sector Finances off track … The strong performance in the economy is slightly at odds with the Public Sector Finances for May, released this week. The UK economy is expanding by just over 3% in the first half of the year. We would expect an improvement in borrowing given the strength of the recovery. Two months into the year and borrowing is off track compared to last year and to plan. In the first two months of the year, total borrowing was up at £24.2 billion compared to £23.2 billion prior year. Strong VAT revenues contributed to a 9% growth in total receipts but expenditure increased by almost 6%, despite a fall in interest payments. Last year’s borrowing figure has been revised to £107.0 billion for the financial year. Good news for the Chancellor but revenues will have to improve and expenditure will have to be contained, if this year’s OBR forecast is to be met. Strong Retail sales in May … Strong retail sales are contributing to the VAT receipts. In May retail sales volumes were up 3.9% compared to last year. This is down on April’s staggering 6.5% growth but we still expect growth of 4.6% in the current quarter and 4.3% for the year as a whole. Internet sales were up by 15%, now accounting for 11.4% of all activity. The online disruption continues. Sales values were up by just 3.2%, contributing to deflation and retail concerns in the High Street. Inflation slows in May … And so it was with the inflation figures. Inflation CPI basis slowed to 1.5% in May, down from 1.8% in April. Service sector inflation was 2.2% and goods inflation held at 0.9%. Falls in transport service costs, notably air fares, provided the largest contribution to the decrease in the rate. Other large downward effects came from food, drinks and clothing. The fall came as something of a surprise, we still expect inflation to track near target (2%) for the year as a whole. Producer Prices no pressure on inflation … No pressure on inflation is evident in the producer price information, released this week. Output prices in May increased by just 0.5% as input costs fell by 5%. Import prices of fuel, oil, food, metals, chemicals, parts, equipment and materials the real story. It is a story of weak international growth in GDP and trade, with slow growth in commodity prices, assisted by the strength of sterling, closing the week above the critical $1.70 level. Monetary Policy and Minutes of the MPC ... So why is Sterling so strong? Statements from Governor Carney that rates may rise “sooner than markets expect" are contrasting with the “Business as Usual” stance from the Federal Reserve. The Fed reduced the forecast GDP 2014 outlook for the US economy to just 2.2% from 3% earlier. Tapering is set to continue but guidelines suggest interest rates will not rise until the second quarter of next year. In the UK, we expect rates to rise in the final quarter of the year. Inflation and earnings suggest that strong growth of itself will not precipitate the rise. The Sterling genie is removing the $1.70 stopper. Who speaks for Sterling? We asked in March last year as the pound headed to the $1.50 level. Sterling look set to test $1.74 in the months ahead unless rate fears are calmed. So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed up against the dollar pushing through resistance at the $1.70 level. Sterling closed up at $1.7010 from $1.696, steady against the Euro at 1.252 (1.253). The Euro strengthened against the dollar at 1.358 from 1.353. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up at $114.70 from $113.07 on Middle East concerns. The average price in June last year was $102.92. The inflation impact cannot be ignored if the a-seasonal pattern persists. Markets, closed up. The Dow closed down at 16,945 from 16,776 and the FTSE was also up at 6,825 from 6,790. UK Ten year gilt yields held at 2.77 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.63 from 2.77 on interest rate trends. Gold moved higher on geo political fears at $1,314 from $1,274. That’s all for this week. Visit the revamped web site. Download our Quarterly Forecast. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. Disclaimer The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. About the Manchester Index™ … The Greater Manchester economy correlates highly with trends in the national economy. The Manchester Index® is an early indicator of trends in both the Manchester and the UK economy. The index is derived from the GM Quarterly Economics Survey which forms part of the British Chambers of Commerce National Survey. Greater Manchester is the largest contributor to this important business survey. We poll 5000 businesses every quarter. As the principal national business survey and the first to be published in each quarter, the results are closely monitored by HM Treasury and the Bank of England Monetary Committee. The GM survey data has a high correlation with the national data. In other key indicators, the unemployment claimant count for example, has a high correlation (over 99%) with the national data set. Our business investment tracker utilises data from capacity and investment intentions to forecast investment in the UK economy. We lag capacity by four quarters and investment intentions by two quarters to model spending.  The first rate hike - it could happen sooner than markets expect … speaking at the Mansion House this week, Mark Carney gave a clear indication UK rates could be hiked this year. “It could happen sooner than markets expect”, the exact wording. A bit tough on the markets, they had placed great confidence in forward guidance. So much for the “unemployment trigger” or the “eighteen indicators” - “watch my lips”, the Governor’s new condition precedent. Last week we suggested - UK rates would have to rise sooner than forward guidance implied. We didn’t have long to wait. The Governor made the move. The markets now believe rates may rise in the final quarter of this year. October would be a fair bet. UK data continues to suggest rates should rise in the Autumn … Construction output increased by a revised 6.7% in the first quarter of the year and by 4.7% in April. We are forecasting growth of almost 6% this year and 5% in 2015. Our forecast for GDP growth is upgraded slightly to 3% from 2.9% this year, as a result of the revisions to the construction data. [Our forecast is unchanged for 2015 - 2.8%]. Manufacturing output increased by 4.4% in April following growth of 3.6% in the first quarter. A strong performance in capital goods output was supported by growth in consumer durables. The march of the makers is picking up the pace but output remains just over 7% below the peak level of 2008. We continue to forecast a recovery with growth of 4% this year. Jobs Data - another strong performance revealed this week. The claimant count fell by 27,000 to 1,086 thousand in May. The reduction over the last three months was 86,000. The average claimant count from 2005 to the middle of 2008 was 880,000. If current trends persist, the pre recession levels will be achieved by the end of the year and job centres will be closing by the end of 2017! The number of vacancies increased to 637,000. This is higher than the average pre recession levels of 634,000. The UV ratio fell to 1.7 from a peak of 3.8 in 2009. The average 2005 - 2008 was 1.4. 33 million are in work [DYDC], an increase of over one million over the last twelve months. Our estimate of spare capacity is 0.6%, compared to the estimates of 1% - 1.5% within the Bank of England. The margin is wafer thin. The “gap” will be exhausted by the final quarter of the year. The labour market is tightening. Rates should be set to rise towards the end of the year. So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed up against the dollar following the comments from the Governor, encountering resistance at the $1.70 level. Sterling closed up at $1.696 from $1.679, up against the Euro at 1.253 (1.231). The Euro softened against the dollar at 1.353 from 1.364. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up at $113.07 from $108.48. The situation in Iraq and the Middle East pushed prices higher. The average price in June last year was $102.92. The inflation impact cannot be ignored if the a-seasonal pattern persists. Markets, closed down on fears of the rate hike in the UK and in the USA. The Dow closed down at 16,776 from 16,899 and the FTSE was also down 6,790 from 6,858. UK Ten year gilt yields rallied at 2.77 (2.63) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.77 from 2.55 on interest rate trends. Gold moved higher on geo political fears at $1,274 from $1,250. That’s all for this week. Visit the revamped web site. Download our quarterly forecast. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  It may have taken some time but households across Britain have finally come to terms the with strength of the recovery. According to GfK, the UK Consumer Confidence Barometer increased to levels last seen in the early part of 2005. Rejoice - we are having a recovery - would have been the Conservative mantra under Prime Minister Thatcher. Confidence in the economic situation of the country, increased to the highest level EVER, since records released in 2004. The propensity to spend is back to levels of 2006, even though the financial situation of households index is still below pre recession numbers. No surprise, perhaps, but with interest rates at such low levels, there is no real uptick in the intentions to save - for the moment at least. Interest Rates set to rise … Maybe households are waiting for the rates to rise. According to Markit®, nearly one in four households expect a rate rise within the next six months … almost half expect rates to rise within the next twelve months. Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit® said, “the recent upbeat news-flow on the economy, strong economic growth in the first quarter, record employment growth and surging house prices, means an increasing number of people think it inevitable that policymakers will be forced into an earlier rate hike than previously envisaged.” Quite right! In fact almost ten per cent, think rates are set to rise within the next three months! So much for forward guidance from the Bank of England. Charlie Bean and Baby Steps … Charlie Bean, the outgoing (as in departing) deputy governor of the Bank of England has suggested “The argument for gradual rises suggests rates should start to go up sooner. The rise could start with “baby steps to avoid making mistakes”. “There’s a case for moving gradually because we won’t be quite certain about the impact of tightening the Bank rate, given everything that has happened to the economy.” The sentiment was also echoed by MPC member Martin Weale, this week. "We can wait a bit longer. How long that 'bit longer' will be I'm not sure.” Ah yes, the merits of forward guidance and a clear steer on monetary policy. Governor Carney will have to whip the MPC troops into line if we are to avoid complete confusion on the direction of rates. The Bank would still have us believe rates will rise in the second quarter of next year. UK rates should rise in the Autumn … In our Greater Manchester Chamber of Commerce Economic Quarterly Outlook, to be released next week, we begin to caution, UK rates should be on the rise in the Autumn, if the present trends in household spending, retail sales and the housing market continue. From an international perspective, the MPC will be reluctant to act ahead of the Fed and the ECB. In the first quarter, US GDP recorded growth of just 2% year on year, postponing, perhaps, the inevitable rate rise. In Europe, fears of deflation may force the ECB to act, to ease, rather than tighten, monetary conditions still further in the June meeting. Japan ends fears of deflation … In Japan, fears of deflation have been assuaged by Abenomics. The solution to fears of falling prices - increase the rate of sales tax and push up prices! Japanese inflation increased by over 3% in April, half of which is explained by the hike in taxes! Fears may later emerge about the slow down in growth, such is the Ground Hog day experience of the lost decade but for the moment, rejoice - the deflationary spiral has been broken in the East! Good News for growth in the UK … Good news for growth in the UK continued this week according to today’s Financial Times. Drugs and prostitution will add £10 billion to the UK economy. Yes, the news that prostitution and drugs will be included in the calculation of the National Accounts from September onwards, adding a new dimension to the “Service Sector” offer. The change will add almost £10 billion to the National Accounts. Hookers will contribute £5.3 billion to “output” (GDP(O)) and drug addicts will add £4.4 billion to the calculation of expenditure (GDP(E). According to ONS research, in 2009, 60,879 prostitutes serviced 25 clients per week at an average spend of £67.19. Don’t you just love economics! If only "tricks" paying 19p could be persuaded to spend more … that would be a recovery! So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed down against the dollar at $1.675 from $1.682 and down against the Euro at 1.230 (1.234). The dollar closed broadly unchanged at 1.362 from 1.363 against the euro and at 101.80 (101.97) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed down at $109.35 from $110.52. The average price in May last year was $102.30. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,682 from 16,593 and the FTSE moved up to 6,852 from 6,815. The markets are set to move higher. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.56 (2.63) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.46 from 2.52. Gold moved down to $1,251 from $1,293. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. 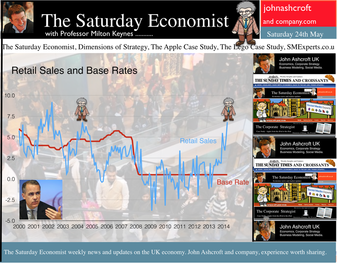 It was one of those heavy weeks for economics releases. Inflation, retail sales, government borrowing plus the eagerly awaited second estimate of GDP. Add in ONS house price information and a heady cocktail of excited headlines was to be expected from the financial pages. Inflation data as expected … It began quietly enough with the inflation data. No surprises, CPI inflation edged up to 1.8% in April from 1.6% in the prior month. The large rise in service sector inflation to 2.8% from 2.3% was offset by a small decline in goods inflation, falling to 0.9% from 1.0%. The uptick was marginally reflected in producer prices, increasing to 0.6% from 0.5%. The more volatile input costs, fell at a slower rate -5.5%, from -6.3% prior month. Energy and oil prices, were again significant in the reduced input costs. Imported metals, chemicals, parts and equipment fell significantly assisted by the 10% appreciation of sterling against the dollar. For the year as a whole, we think inflation will hover close to the target for the best part of the year. The risk remains to the upside in the final quarter. A rise in international prices, and domestic demand, boosted by compression in the labour market is likely to push prices higher. No risk of deflation on the UK horizon, a real risk to the upside is developing. House Prices .. UK house prices increased, according to the ONS data, by 8% in the twelve months to March. “The house market may derail the recovery", the headline. “Carney believes that house prices are the biggest risk to the economy” the great caution. No matter, that house prices increased by over 9% in the prior month or that house prices outside London are increasing by just 4% on average. In the North West prices increased by just over 3%, in Scotland prices hardly increased at all. In London, house prices increased by 17%. Foreign cash buyers at the top end of the market may be confusing the overall trend. However, significant volume and price escalation in the mid tier market is also impacting on price averages. Governor Carney has made it clear interest rates will not rise to combat rising house prices. The remit to action lies with the Financial Policy Committee. Already, action has already been taken to modify the Funding for Lending Scheme away from mortgage lending. Discussions between the Bank and Treasury will continue to consider modifications to the “Help to Buy Scheme”. Implementation of the Mortgage Market Review will also curb lending into 2014. There is a structural problem in the housing market. Mark Carney, Governor of Threadneedle Street, points out that Canada has half the population of the UK but builds twice as many houses. No wonder there is a supply issue. But is the Bank of England prepared to help out? Not really. The Little Old Lady will not turn a sod, grab a hod nor build a single house this year. “We are not in the business of building houses” the Governor’s mantra. The Bank of England will not build a single house in this cycle but neither will it allow the housing market to derail the recovery, provoking a premature move in base rates. Retail Sales … Retail sales figures, on the other hand, suggest rates may have to rise much sooner than expected. Retail sales volumes increased by 6.8% in April compared to prior year. It was May 2004 when retail sales volumes increased at a similar rate. Base rates were 4.75% at the time rising to over 5% within eighteen months. Retail sales values increased by just over 6%. Online sales increased by 13%, accounting for 11% of total action. Consumer confidence is back to the pre recession levels, car sales are up by 8% this year and retail sales are soaring. From a UK perspective, rates should be on the move by the Autumn of this year. The MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and the ECB. The international context suggests the rate rise may be delayed until the second quarter of 2015. Thereafter, for those who would argue the forward horizon has 2.5% cap, the retail sales figures and base rate history should provide a warning of surprises to come. GDP Second Estimate … No surprises in the second estimate of GDP release for Q1. No revisions. The UK economy grew by 3.1% boosted by an 8% surge in investment activity. Manufacturing and Construction increased by over 3% and 5% respectively. The economy is rebalancing … well a little bit! Our May Quarterly Economics Update on behalf of GM Chamber of Commerce is released next week. The outlook for the year remains broadly unchanged. We expect the UK economy to grow by around 3% this year and 2.8% in the following year. The surge in retail activity has been a surprise, as is the continued strength in employment. The outlook remains much the same. Growth up, inflation rising slightly, employment increasing and borrowing, despite the blip in April, set to fall. Just the trade figures will continue to disappoint as we have long pointed out. So what happened to sterling? The pound closed broadly unchanged against the dollar at $1.682 from $1.683 and up against the Euro at 1.234 (1.227). The dollar closed at 1.363 from 1.370 against the euro and at 101.97 (101.54) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up at $110.52 from $109.91. The average price in May last year was $102.3. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,593 from 16,447 but the FTSE adjusted to 6,815 from 6,855. The markets are set to move, the push before the summer rush perhaps. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.63 (2.56 and US Treasury yields closed at 2.52 from 2.51. Gold was unchanged at $1,293 from $1,293. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  The Bank of England Inflation Report - May - So when will rates rise? Q2 2015 still the best bet. The final whistle not for some time yet! The Bank of England Inflation Report was released this week. It was all so predictable. The Governor’s opening remarks explained, “The overall outlook for GDP growth and inflation in this report is little changed from February. The UK economy continues to perform strongly. Having increased by more than 3% in the past year, output is now close to regaining the pre-crisis level. 700,000 more people are in work than a year ago and inflation is below, but close to, the 2% target. And so it proved. The strong labour market performance continued into April. The claimant count rate fell by 25,000, to a rate of 3.3%. The wider LFS data (to March) also reflected the improvement with a fall in the overall rate to 6.8%. On current trends the job centres really will be closing in 2017! The MPC expectations are for growth to increase by 3.2% in the second quarter and by 3.4% for the year as a whole, with continued expansion in household spending. Spending will be supported by an increase in real wages as inflation remains close to target and earnings increase moderately, with a gradual improvement in productivity. The MPC obsession with spare capacity continues. “While there is a range of views on the Committee, the best collective judgement is the margin of spare capacity is around 1% to 1.5% of GDP.” Charlie Bean is not entirely convinced about the “fuzzy concept” of spare capacity. “There is a real danger of spurious precision and the pretence of knowledge in this area” said the Deputy Governor. Quite so. That and many others perhaps! Does spare capacity impact on inflation prospects? Not so much. International inflationary pressures are key to current price trends and for the moment remain subdued. “The global picture is consistent with muted external inflationary pressures which, coupled with sterling’s appreciation, will moderate CPI inflation in the near term” said the Governor. Inflation has fallen sharply since the Autumn and the outlook for inflation in the medium term remains benign. A benign inflation outlook which will avoid undue pressure, in the short term, to increase rates, despite the strong growth figures and the buoyant housing market. So what of rates? The strength of the recovery has moved the economy “closer to the point at which interest rates will have to rise”, the official statement. So when will rates rise? In February, the MPC were happy to attach some credence to the market view that rates would begin to rise in the second quarter of next year. If anything the view in May is slightly more “dovish” or certainly more obtuse. “Our guidance is giving businesses and households confidence that we won’t take risks with price stability, financial stability, or the incipient expansion. It will promote the recovery in business investment, productivity and real wages, that a sustained expansion demands.” Rates are still unlikely to move until the second quarter of next year, the implication. As we explained last week, the MPC will be reluctant to move ahead of the Fed and the ECB. Forward guidance then lapsed into sporting analogy as the governor explained : “Securing the recovery is like making it through the qualifying rounds of the World Cup. That is an achievement but not the ultimate goal. The real tournament is just beginning and the prize is a strong, sustained and balanced expansion.” Yes the the Governor is laying out his team formation for the tournament ahead . “A flat back four with growth, inflation, unemployment and borrowing all heading in the right direction. Two strikers up front, household spending, with support to come from business investment. Some confusion in mid field from the housing market but no mention of exports and rebalancing. So expect the odd own goal from the trade performance, errant on the wing, as we move into the final stages of the competition. The Governor, for now, is not “taking away the punchbowl as the match gets going”. Far from it, you may continue to consume alcohol on the terraces, well into the final stages. Base rates are not expected to rise anytime soon. Q2 next year still the best bet. The final whistle will not be blown for some time yet.” So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed broadly unchanged against the dollar at $1.683 from $1.685 and up against the Euro at 1.227 (1.224). The dollar closed at 1.370 from 1.375 against the euro and at 101.54 (101.18) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed up at $109.91 from $108.16. The average price in May last year was $102.3. Markets, the Dow closed down at 16,447 from 16,544 but the FTSE closed up at 6,855 from 6,821. The markets are set to move, the push before the summer rush. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.56 (2.68) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.51 from 2.62. Gold moved up slightly $1,293 from $1,287. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.  UK … This week, the Bank of England’s Monetary Policy Committee voted to maintain Bank Rate at 0.5%. The Committee also voted to maintain the stock of QE assets at £375 billion. No real surprise, UK rates are expected to remain on hold until the second quarter of 2015. For the moment, UK policy is relatively clear cut. USA … Over in the USA, matters became a little more diffuse. Tapering is expected to continue, concluding the asset purchase programme in September or October this year. But then what happens next? In March, Janet Yellen head of the Fed, gave a clear indication US rates would begin to rise within six months of the end of tapering. Markets reacted badly and the FOMC was minded to recant. This week, testifying before the Joint Economic Committee of the U.S. Congress, Chairman Kevin Brady pushed pushed Yellen for more clarity on when the FOMC would raise interest rates. The Fed chair would not be drawn on this occasion. “There is no mechanical formula for when that would occur” - the somewhat mechanical and evasive response. Oh yes, a month is a long time in the formulation of monetary policy. Europe … In Europe, Mario Draghi, President of the ECB, faced the opposite dilemma. With modest growth forecast for Euroland this year, inflation below target at less than 1% and a Euro strengthening against the dollar ($1.375), the Italian banker is under pressure to alleviate European monetary conditions still further. Playing for time, Draghi stated policy makers at the bank were comfortable with action in early June. Action awaits the “staff projections” for growth and inflation next month, before considering the next step. Draghi must hope forecasts are revised upwards. Having promised to “do what it takes” to stimulate growth, the President is clearly at a loss, as to what can be done next. A reduction in base rates to the zero floor would have little economic impact. Experimentation with negative rates is a high risk strategy. The move would thrill academic economists but cause trauma in the markets. This is no time for experimentation with central bank novelties. QE is muted as a possibility but with German and French long rates at 1.45% and 1.9%, there seems little cause to push rates lower. Ten year bond rates in Spain and Italy are this week trading within 25 basis points of UK gilts. MPC Dilemma … So here in a way is the dilemma for the MPC. The UK economy is growing at 3% a year, unemployment is falling at such a rate, we may have to close the job centres in 2017. Inflation is below target but as Mario Draghi pointed out this week, it is the weakness in international commodity prices, oil, energy and food, the real determinants of low inflation. Low inflationary pressure exacerbated or assisted by the rise in the Euro (and Sterling) against the Dollar. The UK is caught in the Dollar Euro vortex, with basic economics pushing monetary policy in opposing directions apparently. The MPC cannot move ahead of the Fed or much in advance of Europe for that matter without pushing Sterling still higher. Deflation the illusion - OECD World Forecasts This month the OECD forecast a recovery in world growth this year to 3.4% in 2014 and almost 4% in 2015. The Euro area is set to grow by 1.2% and 1.7% over the period. Euro inflation is set to rise above 1.2% next year. Commodity prices (base metals) are demonstrating a price basing action, Oil Brent Crude basis is trading ahead of last year. The international price profile can change quickly and dramatically. The threat of deflation - an illusion - which may quickly dissipate. A strong ECB president should do nothing. The US must accept rates will rise within six months of the end of tapering. This would leave the MPC free to begin the inevitable rate rise in the second quarter of next year. Want to here more, don’t miss the quarterly economics presentation on Wednesday at DWF next week. The multi media roadshow rolls on! So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed unchanged against the dollar at $1.685 from $1.687 and up against the Euro at 1.224 (1.217). The dollar closed at 1.375 from 1.377 against the euro and at 101.18 (102.23) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed at $108.16 from $108.50. The average price in May last year was $102.3. Markets, the Dow closed unchanged at 16,544 from 16,542 and the FTSE also closed up at 6,821 from 6,814. The markets are set to the move, the push before the rush. UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.68 (2.72) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.62 from 2.72. Gold moved down $1,287 from $1,296. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. It's just for fun, what's not to like! Dr John Ashcroft is The Saturday Economist.  GDP Figures Q1 … UK growth in the first quarter of 2014 was an impressive 3.1% year on year with significant growth in construction, manufacturing and the service sector. [According to the preliminary estimate from the Office for National Statistics released this week.] Construction growth increased by 5.1% in the quarter and manufacturing output increased by 3.5%. Service sector output was up by 2.9% with continued strong growth in distribution, hotels, and leisure (4.9%). The business and financial services sector increased by 3.6%. The outturn is more or less in line with our estimates in the Quarterly Economics Outlook released in March. Following the latest data, we have lowered our forecasts for growth in the construction sector for the year as a whole and increased our estimate of growth in manufacturing. The overall GDP position remains unchanged. We still forecast GDP growth of 2.9% in 2014 and 2.8% in 2015. Growth continues into Q2 … The good news continued this week, with the latest Markit/CIPS PMI® survey data on manufacturing and construction. In April the UK manufacturing sector maintained a robust start to the year. At 57.3, the seasonally adjusted index rose to a five-month high and registered one of the best readings over the past three years. Construction output continued to increase in April, albeit at the slowest pace for six months. The index recording of 60.2 is down from the peaks at the turn of the year but still ahead of the long run average of 54.3. Residential construction was the best performing area of activity. The rate of expansion in April remained one of the fastest seen over the past ten years … just as well! House Prices - increase into double figures … House prices increased by over 10% according to the latest figures from Nationwide. Robert Gardner, Nationwide's Chief Economist said: “After several months of moderation, the pace of house price growth picked up in April. Annual house price growth reached double digits for the first time in four years, with the price of a typical home 10.9% higher than April 2013. Still much to be done in construction however, “The upturn in construction of new homes continues to lag far behind the upturn in demand, with the number of new homes being built in England still around 40% below pre crisis levels.” Sir Jon Cunliffe, Deputy Governor of the Bank of England, expressed some concerns about the housing market in a speech in London this week. “The question for the Financial Policy Committee, is whether the sustained momentum in the housing market will lead to unsustainable growth in household indebtedness, undermining the resilience of the financial system. The growing momentum in the housing market is now the brightest light on the dashboard of warning lights.” You have been warned! Growth in the USA ... In the USA, growth in the first quarter was up by 2.3% year on year (0.1% quarter on quarter). The relatively disappointing number was attributed to a severe winter and much bad, wet weather. The Federal reserve derived some consolation from the strength of the jobs numbers released this week. In April, the number of non farm payroll jobs increased by almost 290,000, the unemployment rate fell to 6.3% and revisions to the employment numbers over the past three months confirmed the strength of the US recovery. Jobs growth over the last three months has averaged almost 240,000. With evidence of a strong performance in employment and household spending, the Federal reserve announced a further reduction in tapering with a reduction in asset purchases to $45 billion per month. Tapering is on track to completion by the September / October this year. Interest rate rises will then ensue possibly within six months. With inflation below target, wages rising by just 1.9% and almost 10 million Americans unemployed, the FOMC will be in no rush to act. So what happened to sterling this week? The pound closed up against the dollar at $1.687 from $1.681 and up against the Euro slightly at 1.217 (1.215). The dollar closed at 1.387 from 1.382 against the euro and at 102.23 (102.15) against the Yen. Oil Price Brent Crude closed at $108.50 from $109.54. The average price in May last year was $102.3. Markets, the Dow closed up at 16,542 from 16,370 and the FTSE also closed up at 6,821 from 6,685. The markets are making the move, the push before the rush, may see the FTSE hit 7000 before the summer sell off! UK Ten year gilt yields closed at 2.72 (2.66) and US Treasury yields closed at 2.72 from 2.67. Gold moved down $1,296 from $1,301. That’s all for this week. Join the mailing list for The Saturday Economist or forward to a friend. John © 2014 The Saturday Economist by John Ashcroft and Company. Experience worth sharing. The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The receipt of this email should not be construed as the giving of investment advice. |
The Saturday EconomistAuthorJohn Ashcroft publishes the Saturday Economist. Join the mailing list for updates on the UK and World Economy. Archives
July 2024
Categories
All
|
| The Saturday Economist |
The material is based upon information which we consider to be reliable but we do not represent that it is accurate or complete and it should not be relied upon as such. We accept no liability for errors, or omissions of opinion or fact. In particular, no reliance should be placed on the comments on trends in financial markets. The presentation should not be construed as the giving of investment advice.
|
The Saturday Economist, weekly updates on the UK economy.
Sign Up Now! Stay Up To Date! | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | |
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed